Design and Technologies
Rationale
Technologies enrich and impact on the lives of people and societies globally. Society needs enterprising students who can make discerning decisions about the development and use of technologies, develop solutions to complex challenges and contribute to sustainable patterns of living. Technologies can play an important role in transforming, restoring and sustaining societies and natural, managed and constructed environments.
The Western Australian Curriculum: Technologies describes two distinct but related subjects:
- Design and Technologies, in which students use design thinking and technologies to generate and produce solutions for authentic needs and opportunities
- Digital Technologies, in which students use computational thinking and information systems to define, design and implement solutions.
In an increasingly technological and complex world, it is important to develop knowledge and skills to analyse and creatively respond to design and/or digital challenges.
Through the practical application of technologies including digital technologies, students develop dexterity and coordination through experiential activities. Technologies motivates young people and engages them in a range of learning experiences that are transferable to family and home, constructive leisure activities, community contribution and the world of work.
Technologies provides students with authentic learning challenges that foster curiosity, confidence, persistence, innovation, creativity, respect and cooperation. These attributes are necessary when using and developing solutions to make sense of complex ideas and relationships in all areas of learning. Technologies helps students to be regional and global citizens, capable of actively and ethically communicating and collaborating.
Design and Technologies
Knowledge, understandings and skills involved in the design, development and use of technologies are influenced by, and can play a role in, enriching and transforming societies and our natural, managed and constructed environments.
The Western Australian Curriculum: Design and Technologies actively engages students in creating quality designed solutions for identified needs and opportunities across a range of technologies contexts. Students consider the economic, environmental and social impacts of technological change and how the choice and use of technologies contributes to a sustainable future. Decision-making processes are informed by ethical, legal, aesthetic and functional factors.
Through Design and Technologies students manage projects, independently and collaboratively, from conception to realisation. They apply design and systems thinking and design processes to investigate ideas, generate and refine ideas, plan, produce and evaluate designed solutions. They develop their ability to generate innovative designed products, services and environments.
Digital Technologies
Digital systems are everywhere, mobile and desktop devices and networks are transforming learning, recreational activities, home life and work. Digital systems support new ways of collaborating and communicating, and require new skills such as computational and systems thinking. Technologies are an essential problem-solving toolset in our knowledge-based society.
The Western Australian Curriculum: Digital Technologies empowers students to shape change by influencing how contemporary and emerging information systems and practices are applied to meet current and future needs. A deep knowledge and understanding of information systems enables students to be creative and discerning decision-makers when they select, use and manage data, information, processes and digital systems to meet needs and shape preferred futures.
Digital Technologies provides students with practical opportunities to use design thinking and to be innovative developers of digital solutions and knowledge. Digital Technologies enables students to become innovative creators of digital solutions, effective users of digital systems and critical consumers of information conveyed by digital systems.
Aims
The Western Australian Curriculum: Technologies aims to develop the knowledge, understandings and skills to ensure that, individually and collaboratively, students:
- investigate, design, plan, manage, create and evaluate solutions
- are creative, innovative and enterprising when using traditional, contemporary and emerging technologies, and understand how technologies have developed over time
- make informed and ethical decisions about the role, impact and use of technologies in the economy, environment and society for a sustainable future
- engage confidently with and responsibly select and manipulate appropriate technologies − materials, data, systems, components, tools and equipment − when designing and creating solutions
- critique, analyse and evaluate problems, needs or opportunities to identify and create solutions.
Design and Technologies
Design and Technologies aims to develop the knowledge, understandings and skills to ensure that, individually and collaboratively, students:
- produce designed solutions suitable for a range of Technologies contexts by selecting and manipulating a range of materials, systems, components, tools and equipment creatively, competently and safely; and managing processes
- understand the roles and responsibilities of people in design and technologies occupations and how they contribute to society.
Digital Technologies
Digital Technologies aims to develop the knowledge, understandings and skills to ensure that, individually and collaboratively, students:
- use computational thinking and the key concepts of abstraction; data collection, representation and interpretation; specification, algorithms and implementation to create digital solutions
- confidently use digital systems to efficiently and effectively transform data into information and to creatively communicate ideas in a range of settings
- apply systems thinking to monitor, analyse, predict and shape the interactions within and between information systems and understand the impact of these systems on individuals, societies, economies and environments.
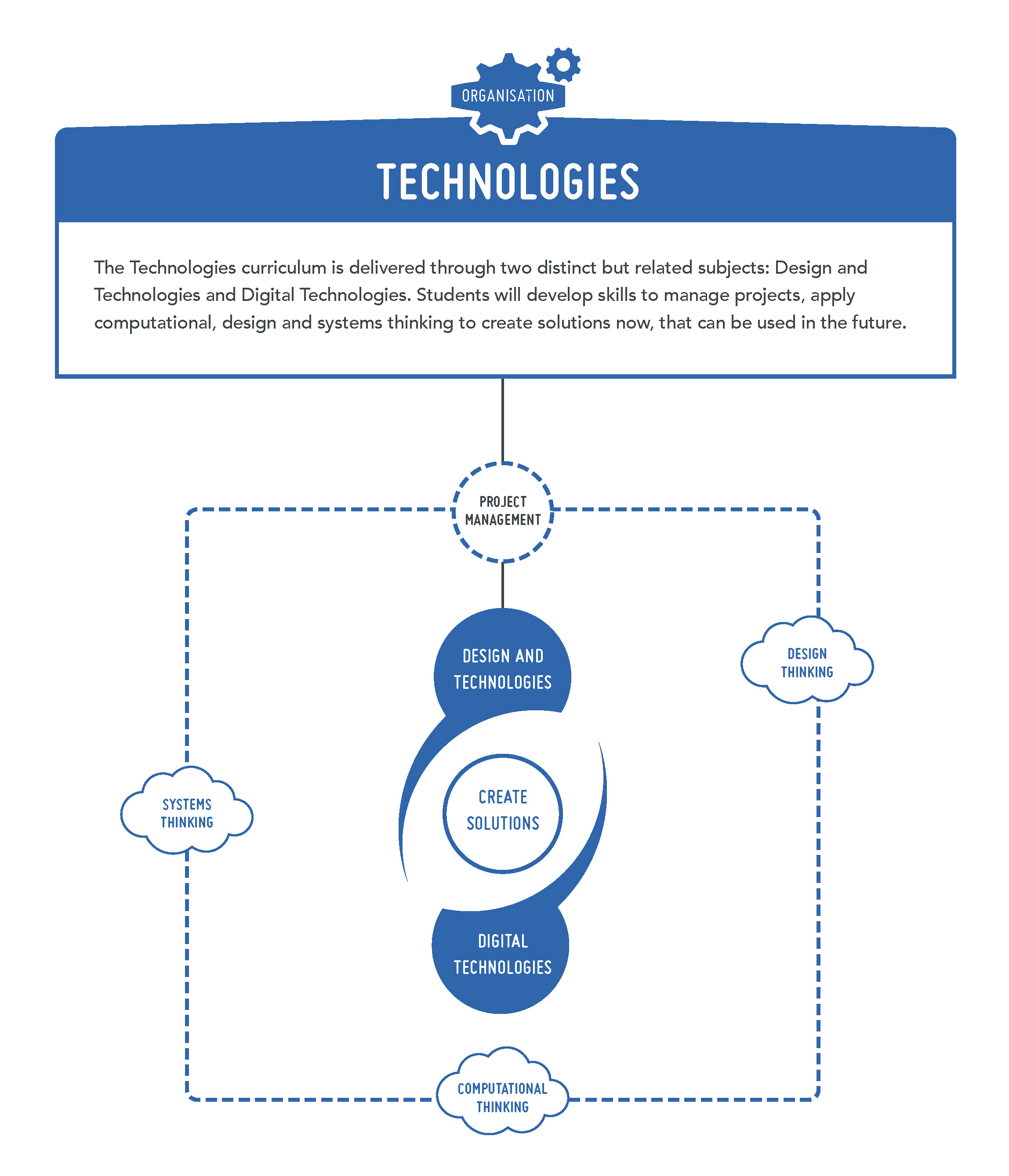
Organisation
Content structure
The Western Australian Curriculum: Technologies learning area comprises two subjects:
- Design and Technologies
- Digital Technologies
The Technologies curriculum is written on the basis that all students will study both Technologies subjects from Pre-primary to the end of Year 8. Within Design and Technologies (Engineering principles and systems; Food and fibre production; Food specialisations; Materials and technologies specialisations), students have the opportunity to study at least one of the contexts.
In Years 9 and 10 the study of Technologies is optional.
In Design and Technologies, it is desirable that schools provide students with the opportunity to engage with all contexts across Pre-primary to Year 10.
In Design and Technologies students learn about technologies in society through different technologies contexts (Engineering principles and systems; Food and fibre production; Food specialisations; and Materials and technologies specialisations) as they create designed solutions.
In Digital Technologies students are provided with practical opportunities to use design thinking and to be innovative developers of digital solutions and knowledge. Digital Technologies is a subject that has a specific curriculum and includes the practical application of the ICT general capability.
The syllabus for each of these subjects describes the distinct knowledge, understanding and skills of each subject and, where appropriate, highlights their similarities and complementary learning. This approach enables students to develop a comprehensive understanding of traditional, contemporary and emerging technologies. It also provides the flexibility, especially in the primary years of schooling, for developing integrated teaching programs that focus on both Technologies subjects and concepts and skills in other learning areas.
Relationship between the strands
Knowledge, understanding and skills in each subject are presented through two related strands:
- Knowledge and understanding
- Processes and production skills
Teachers select technologies-specific content from the Knowledge and understanding strand and students apply skills from the Processes and production skills strand to that content.
The common strand structure provides an opportunity to highlight similarities across the two subjects.
Knowledge and understanding
| Design and Technologies | Digital Technologies |
Technologies and society
Technologies and design across a range of technologies contexts:
| Digital systems
Representation of data
|
Table 1: Outlines the focus of the knowledge and understanding across the two Technologies subjects
Processes and production skills
| Design and Technologies | Digital Technologies |
Creating solutions by:
| Collecting, managing and analysing data
Digital implementation
Creating solutions by:
|
Table 2: Outlines the focus of the processes and production skills across the two Technologies subjects
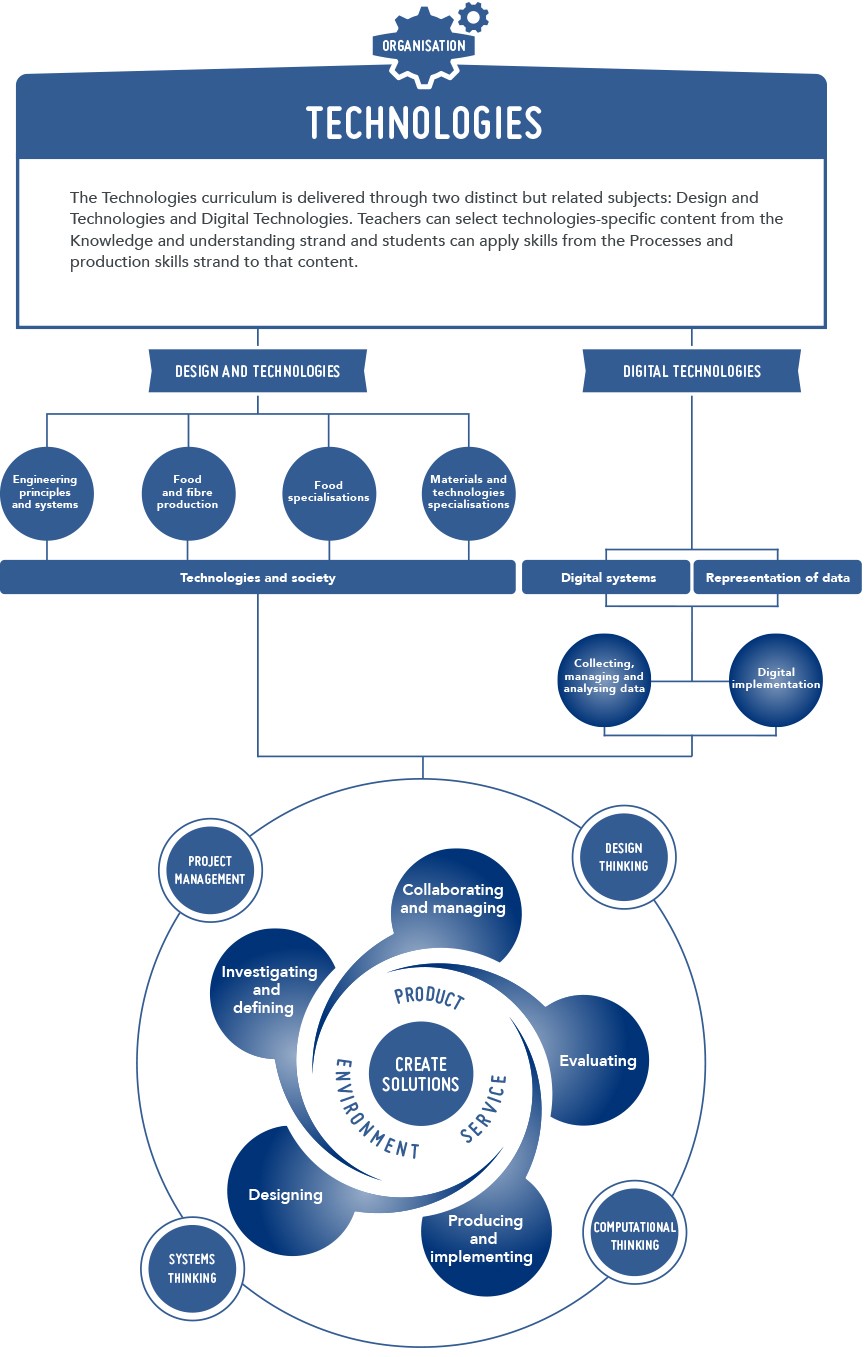
|
| Figure 2: The organisation of content in the Technologies curriculum |
Year level descriptions
Year level descriptions provide an overview of the key concepts addressed, along with core content being studied at that year level. They also emphasise the interrelated nature of the two strands and the expectation that planning will involve integration of content from across the strands.
Content descriptions
Content descriptions set out the knowledge, understanding and skills that teachers are expected to teach and students are expected to learn. They do not prescribe approaches to teaching. The core content has been written to ensure that learning is appropriately ordered and that unnecessary repetition is avoided. However, a concept or skill introduced at one year level may be revisited, strengthened and extended at later year levels as needed.
Additional content descriptions are available for teachers to incorporate in their teaching programs. Schools will determine the inclusion of additional content, taking into account learning area time allocation and school priorities.
The additional content will not be reflected in the Achievement Standards.
Achievement standards
From Pre-primary to Year 10, achievement standards indicate the quality of learning that students should typically demonstrate by a particular point in their schooling. An achievement standard describes the quality of learning (e.g. the depth of conceptual understanding and the sophistication of skills) that would indicate the student is well-placed to commence the learning required at the next level of achievement.
Glossary
A glossary is provided to support a common understanding of key terms and concepts included in the core content.
Student Diversity
The School Curriculum and Standards Authority is committed to the development of a high-quality curriculum for all Western Australian students that promotes excellence and equity in education.
All students are entitled to rigorous, relevant and engaging learning programs drawn from the Western Australian Curriculum: Technologies. Teachers take account of the range of their students' current levels of learning, strengths, goals and interests and make adjustments where necessary. The three-dimensional design of the Western Australian Curriculum, comprising learning areas, general capabilities and cross-curriculum priorities, provides teachers with flexibility to cater for the diverse needs of students across Western Australia and to personalise their learning.
Students with disability
The Disability Discrimination Act 1992 and the Disability Standards for Education 2005 require education and training service providers to support the rights of students with disability to access the curriculum on the same basis as students without disability.
Many students with disability are able to achieve educational standards commensurate with their peers, as long as the necessary adjustments are made to the way in which they are taught and to the means through which they demonstrate their learning.
In some cases, curriculum adjustments are necessary to provide equitable opportunities for students to access age-equivalent content in the Western Australian Curriculum: Technologies. Teachers can draw from content at different levels along the Pre-primary – Year 10 sequence. Teachers can also use the general capabilities learning continua in Literacy, Numeracy and Personal and social capability to adjust the focus of learning according to individual student need.
Adjustments to the delivery of some practical aspects of lessons will be necessary to ensure some students with physical disability can access, participate, and achieve on the same basis as their peers. This might involve students using modified tools, materials or equipment to create solutions. Teachers may also need to consider adjustments to assessment of students with disability to ensure student achievement and demonstration of learning is appropriately measured.
English as an additional language or dialect
Students for whom English is an additional language or dialect (EAL/D) enter Western Australian schools at different ages and at different stages of English language learning and have various educational backgrounds in their first languages. While many EAL/D students bring already highly developed literacy (and numeracy) skills in their own language to their learning of Standard Australian English, there are a significant number of students who are not literate in their first language, and have had little or no formal schooling.
While the aims of the Western Australian Curriculum: Technologies are the same for all students, EAL/D students must achieve these aims while simultaneously learning a new language and learning content and skills through that new language. These students may require additional time and support, along with teaching that explicitly addresses their language needs. Students who have had no formal schooling will need additional time and support in order to acquire skills for effective learning in formal settings.
Gifted and talented students
Teachers can use the Western Australian Curriculum: Technologies flexibly to meet the individual learning needs of gifted and talented students.
Teachers can enrich students' learning by providing them with opportunities to work with learning area content in more depth or breadth (e.g. using the additional content descriptions); emphasising specific aspects of the general capabilities learning continua (e.g. the higher order cognitive skills of the critical and creative thinking capability); and/or focusing on cross-curriculum priorities. Teachers can also accelerate student learning by drawing on content from later year levels in the Western Australian Curriculum: Technologies and/or from local, state and territory teaching and learning materials. Technologies education pedagogy and project-based learning allows students to take greater responsibility for their learning and allows them to make decisions based on findings from research, experimentation and testing of design ideas.
Ways of Teaching
The 'ways of teaching' aim to support teachers with planning for curriculum delivery across the years of school, with the teaching in each year extending learning in previous years.
The 'ways of teaching' complement the principles of teaching and learning in the Western Australian Curriculum and Assessment Outline (http://k10outline.scsa.wa.edu.au/). The principles focus on the provision of a school and class environment that is intellectually, socially and physically supportive of learning. The principles assist whole-school planning and individual classroom practice.
The Technologies learning area is made up of two distinct subjects Design and Technologies and Digital Technologies. The content is presented through the interrelated strands of Knowledge and understanding and Processes and production skills. The strands are different in each subject; with common threads to allow for integration between the Technologies subjects. Knowledge and understanding is taught in combination with the processes and production skills.
The teaching of Technologies requires learning experiences which allow students to:
- develop systems, design and computational thinking
- create digital solutions
- create product, service and environment designed solutions.
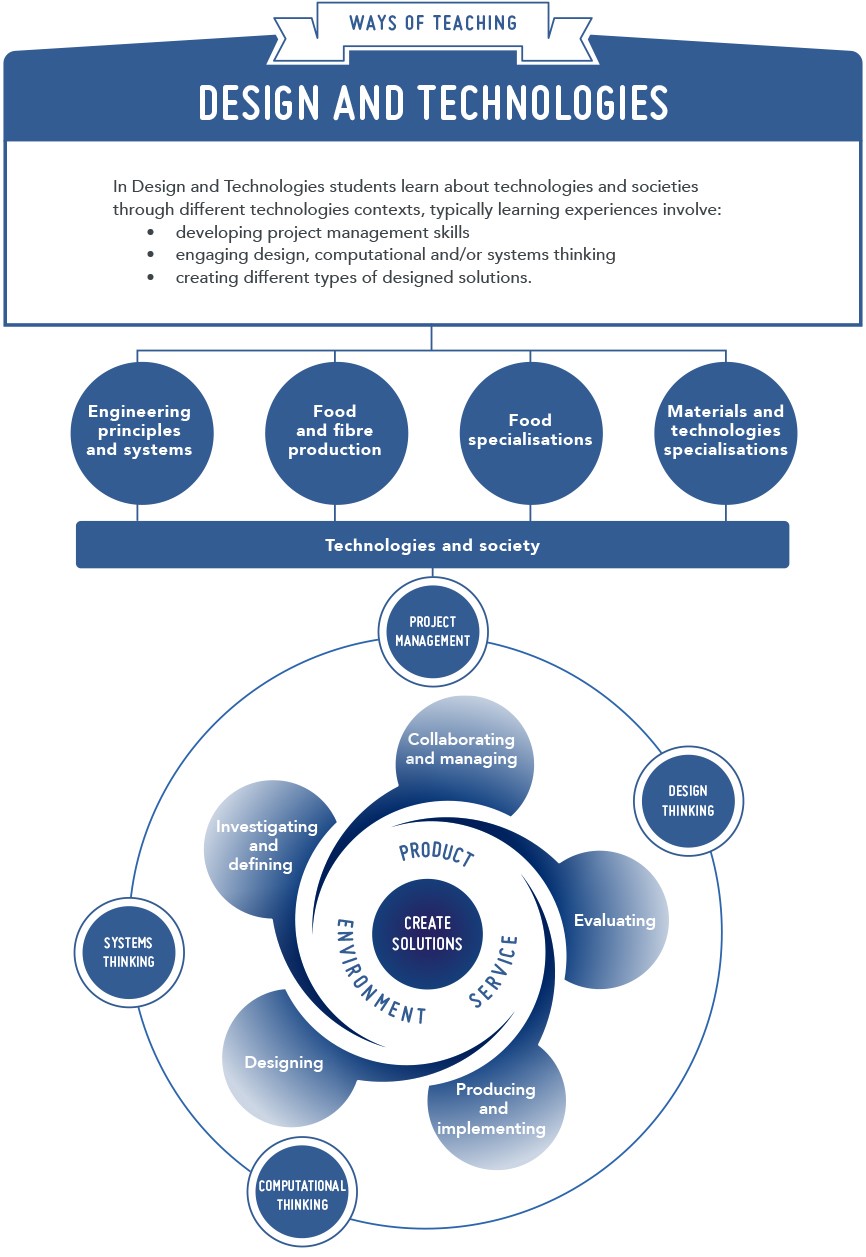
Design and Technologies
In Design and Technologies students learn about technologies and societies through different technologies contexts. In each year students will be given opportunities to create designed solutions in at least one of the technologies contexts below:
- Engineering principles and systems – in this context the focus is on how forces can be used to create light, sound, heat, movement, control or support in systems
- Food and fibre production – in this context the focus is on the process of producing food or fibre as natural materials for the design and development of a range of products. Fibre includes materials from forestry (Food and fibre production includes Food specialisations from Pre-primary to Year 4)
- Food specialisations – in this context the focus is on the application of nutrition principles and knowledge about the characteristics and properties of food to food selection, preparation; and contemporary technology-related food issues
- Materials and technologies specialisations – in this context the focus is on a broad range of traditional, contemporary and emerging materials and specialist areas that typically involve extensive use of technologies, this includes materials such as, textiles, metal, wood and plastics.
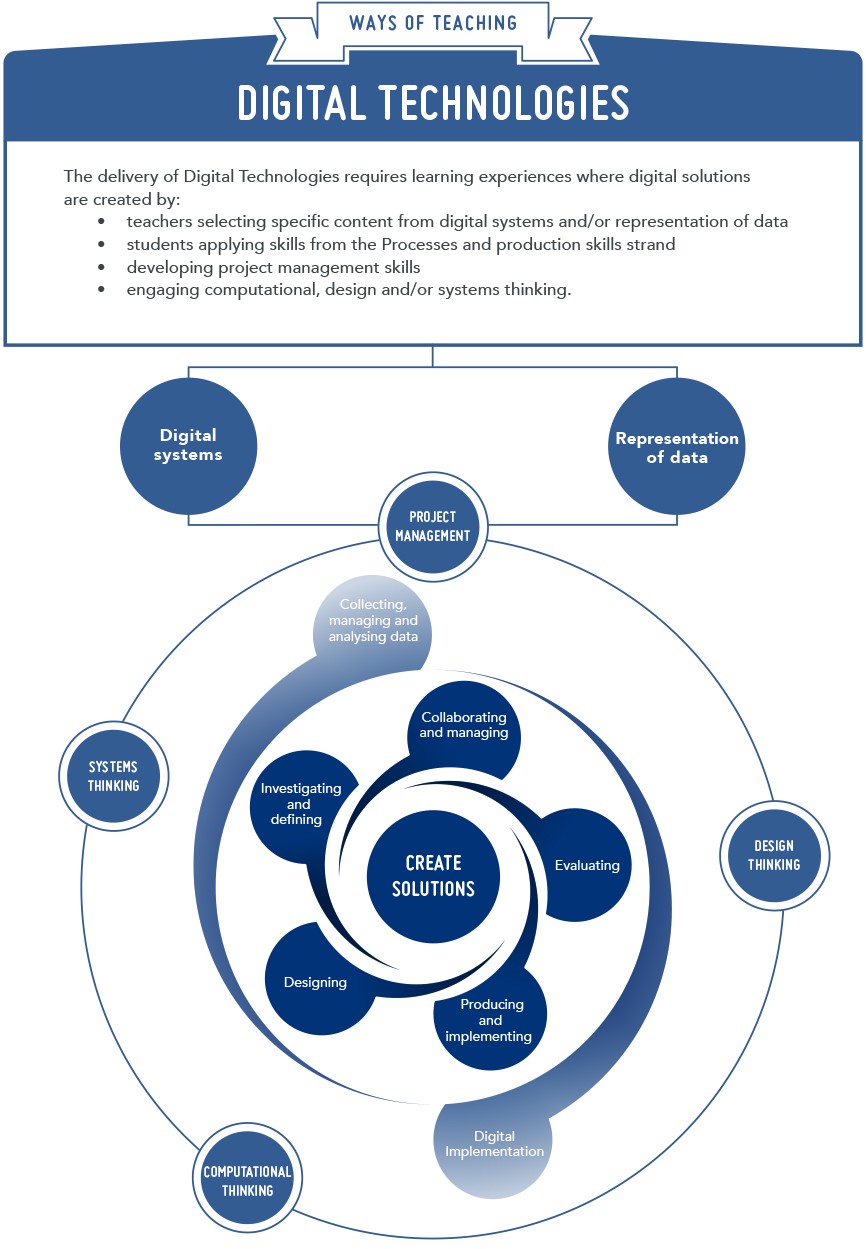
Digital Technologies
Digital Technologies is a subject that has a specific curriculum and includes the practical application of the ICT general capability.
In Digital Technologies, students develop an understanding of the characteristics of data, digital systems, audiences, procedures and computational thinking. They apply this when they investigate, communicate and create digital solutions.
The ICT capability involves students in learning to make the most of the technologies available to them, adapting to new ways of doing things as technologies evolve, and limiting the risks to themselves and others in a digital environment.
The clear difference between the Digital Technologies curriculum and the ICT general capability is that the capability helps students to become effective users of digital technologies while the Digital Technologies curriculum helps students to become confident developers of digital solutions.
In the primary years, the Technologies subjects are often interrelated and connected through other learning areas. When programming, teachers can use the Technologies learning area as a basis for the practical application and development of concepts from other learning areas. For example, students' mathematical ability to solve problems involving linear equations can be used in Technologies when investigating quantitative relationships and designing algorithms.
In the secondary years, Technologies is typically a specialist area, with both subjects and each of the contexts taught by specialist teachers.
When developing teaching and learning programs:
- the teacher identifies the prior knowledge of students to establish a starting point for the learning
- the teacher defines the subject and context for the learning experience with reference to the content descriptions. (For example, Design and Technologies – Food and fibre production)
- the teacher and students identify the problem, situation or need that requires a solution, considering resources available.
Teachers generate meaningful learning activities to facilitate creating solutions, for example, students:
- reflect on actions to refine working processes and develop decision making skills
- evaluate how well systems and/or products meet current and future sustainability needs
- manage collaborative projects
- apply appropriate social, ethical and technical protocols
- use a range of delivery modes such as audio, visual and practical
- develop skills to produce solutions to problems
- investigate emerging technologies
- identify 'real world problems'
- investigate 'problem, situation or needs' for which to find a solution
- engage in experiences that are transferable to family and home, community contribution and the world of work
- use critical and creative thinking to weigh up possible short and long term impacts
- reflect upon existing designs to source ideas for future solutions
- play and experiment with technologies to investigate possible solutions.
For information on how to collect evidence to inform planning for ongoing learning experiences in Technologies refer to 'Ways of Assessing'.
Ways of Assessing
The 'ways of assessing' complement 'ways of teaching' and aim to support teachers in developing effective assessment practice in Technologies.
The 'ways of assessing' also complement the principles of assessment contained in the Western Australian Curriculum and Assessment Outline. The assessment principles, reflective questions and assessment snapshots support teachers in reflecting on their own assessment practice in relation to each of the assessment principles. Here teachers will find:
- background information for each principle
- reflective questions
- guidance for addressing the principle within their own assessment practice.
Refer to the Western Australian Curriculum and Assessment Outline (http://k10outline.scsa.wa.edu.au/) for further guidance on assessment principles, practices and phases of schooling.
The key to selecting the most appropriate assessment is in the answers to several reflective questions. For example:
- How do you use assessment as the starting point of your lesson planning?
- Do your assessments have a clear purpose?
- Do you design assessment tasks in a way that meets the dual purposes of formative and summative assessment?
- How do you use your observations of students (during the course of classroom activities, in assignments and in tests) to determine how learning can be improved?
- How do you identify students' misconceptions or gaps in their learning?
- How do you identify the next skill or understanding a student or group of students needs to learn?
- What information do you collect to evaluate your own teaching?
- How do you work with colleagues to evaluate student achievement data and how does this work inform your teaching?
- What range of evidence do you draw on when you report student performance and evaluate your teaching?
In the Western Australian Curriculum: Technologies the two strands, Knowledge and understanding and Processes and production skills, are interrelated and inform and support each other. When developing assessment strategies, teachers combine components of the strands in different ways to provide students with opportunities to demonstrate their knowledge and understanding through the practical application of their skills, (e.g. students may be asked to consider the implications of technologies in society when designing a solution to a problem, situation or need). The assessment experiences and evidence collected may look different for individual tasks as the assessment strategies should match the design brief and be reflective of individual students' understandings and interpretation of the solution they are creating.
Refer to the Judging Standards tool in the Western Australian Curriculum and Assessment Outline (http://k10outline.scsa.wa.edu.au/home/judging-standards) when reporting against the Achievement Standards; giving assessment feedback; or explaining the differences between one student's achievement and another's.
The following table provides examples of assessment strategies which can enable teachers to understand where students are in their learning. Assessments should also be based on the integration of a range of types and sources of evidence.
Examples of assessment strategies | Examples of sources of evidence |
|---|---|
Observations | The observations of student understandings and process and production skills through the use of anecdotal notes, checklists, photographs, videos or recordings. |
Group activities | Collaborating and managing is one of the production and processes skills, this needs to be actively programmed for and assessed in accordance with the relevant year's content description. During group work, teachers should stop at key points to check individual student understanding. |
Videos or audio recordings | The recording of student achievement in physical and verbal activities such as role-plays, performances, speeches, play-based learning, debates or online discussions. |
Fieldwork and practical (authentic) evidence | The demonstration of learning through activities such as virtual and actual fieldwork, to inform the creation of digital and designed solution. |
Portfolios and work samples | Collections of student work that provide long-term documentation of student progress and achievement. Portfolios may be subject area specific or contain a range of work undertaken by the student and be evidence of project management. |
Tests or quizzes | These may include verbal questioning, multiple choice, short answer responses or open-ended questions that require longer, sustained written responses. |
Written work | This includes short and extended written tasks. These may take the form of short responses such as worksheets and sentence or paragraph answers. Longer responses may include essays, information reports or imaginative texts such as narratives and journal entries. Students may also conduct investigations in which they must develop questions; gather, analyse and evaluate information; communicate on findings and reflect upon conclusions. |
Graphic organisers | Frameworks, including digital, that help structure thinking. They make thinking processes visible by showing connections between data. Examples include concept maps, flowcharts and cause-and-effect patterns. |
Visual representations | The demonstration of learning through, algorithms, tables, graphs, diagrams, posters, brochures, photographs and other digital media (e.g. slides, animations, blogs). |
Performances or oral presentations | The demonstration of learning in role-play, speeches, simulations, debates and structured discussions. |
Conferences | Discussions or interviews that are conducted either face-to-face, online or via audio and video recordings. |
Self-assessments and evaluations and student journals | The self-reflection of achievement and progression towards goals. It allows for metacognitive thinking about their learning and personal reflection upon their strengths and weaknesses. Journals provide personal accounts of student responses to learning activities, experiences and understandings. This should be guided by the relevant year's content description on Evaluating. |
Peer assessments | Individuals, peers or a group of peers provide evaluative feedback on performance or activity. |
General Capabilities
The general capabilities encompass the knowledge, skills, behaviours and dispositions that will assist students to live and work successfully in the 21st century. Teachers may find opportunities to incorporate the capabilities into the teaching and learning program for Technologies. The general capabilities are not assessed unless they are identified within the content.
Literacy
Across the Western Australian Curriculum, students become literate as they develop the knowledge, skills and dispositions to interpret and use language confidently for learning and communicating in and out of school and for participating effectively in society. Literacy involves students in listening to, reading, viewing, speaking, writing and creating oral, print, visual and digital texts, and using and modifying language for different purposes in a range of contexts.
In Technologies, students develop literacy as they learn how to communicate ideas, concepts and detailed proposals to a variety of audiences; read and interpret detailed written instructions for specific technologies, often including diagrams and procedural writings such as software user manuals, design briefs, patterns and recipes; prepare accurate, annotated engineering drawings, software instructions and coding; write project outlines, briefs, concept and project management proposals, evaluations, engineering, life cycle and project analysis reports; and prepare detailed specifications for production.
By learning the literacy of technologies students understand that language varies according to context and they increase their ability to use language flexibly. Technologies vocabulary is often technical and includes specific terms for concepts, processes and production. Students learn to understand that much technological information is presented in the form of drawings, diagrams, flow charts, models, tables and graphs. They also learn the importance of listening, talking and discussing in technologies processes, especially in articulating, questioning and evaluating ideas.
Numeracy
Across the Western Australian Curriculum, students become numerate as they develop the knowledge and skills to use mathematics confidently across all learning areas at school, and in their lives more broadly. Numeracy involves students in recognising and understanding the role of mathematics in the world and having the dispositions and capacities to use mathematical knowledge and skills purposefully.
The Technologies curriculum gives students opportunities to interpret and use mathematical knowledge and skills in a range of real-life situations. Students use number to calculate, measure and estimate; interpret and draw conclusions from statistics; measure and record throughout the process of generating ideas; develop, refine and test concepts; and cost and sequence when making products and managing projects. In using software, materials, tools and equipment, students work with the concepts of number, geometry, scale, proportion, measurement and volume. They use three-dimensional models, create accurate technical drawings, work with digital models and use computational thinking in decision-making processes when designing and creating best-fit solutions.
Information and communication technology (ICT) capability
Across the Western Australian Curriculum, students develop ICT capability as they learn to use ICT effectively and appropriately to access, create and communicate information and ideas; solve problems; and work collaboratively in all learning areas at school, and in their lives beyond school. The capability involves students in learning to make the most of the technologies available to them, adapting to new ways of doing things as technologies evolve, and limiting the risks to themselves and others in a digital environment.
In Digital Technologies, students develop an understanding of the characteristics of data, digital systems, audiences, procedures and computational thinking. They apply this when they investigate, communicate and create digital solutions. Students learn to formulate problems, logically organise and analyse data and represent them in abstract forms. They automate solutions through algorithmic logic. Students decide the best combinations of data, procedures and human and physical resources to generate efficient and effective digital solutions. They create digital solutions that consider economic, environmental and social factors.
In Design and Technologies, key ICT concepts and skills are strengthened, complemented and extended. Students become familiar with and gain skills using a range of software applications and digital hardware that enable them to realise their design ideas. Students use ICT when they investigate and analyse information and evaluate design ideas and communicate and collaborate online. They develop design ideas; generate plans and diagrams to communicate their designs and produce solutions using digital technologies, for example creating simulations, drawings and models and manufacturing solutions (from basic drawing programs to computer-aided design/manufacture and rapid prototyping).
Critical and creative thinking
Across the Western Australian Curriculum, students develop capability in critical and creative thinking as they learn to generate and evaluate knowledge, clarify concepts and ideas, seek possibilities, consider alternatives and solve problems. Critical and creative thinking are integral to activities that require students to think broadly and deeply using skills, behaviours and dispositions such as reason, logic, resourcefulness, imagination and innovation in all learning areas at school and in their lives beyond school.
Students develop capability in critical and creative thinking as they imagine, generate, develop and critically evaluate ideas. They develop reasoning and the capacity for abstraction through challenging problems that do not have straightforward solutions. Students analyse problems, refine concepts and reflect on the decision-making process by engaging in systems, design and computational thinking. They identify, explore and clarify technologies information and use that knowledge in a range of situations.
Students think critically and creatively about possible, probable and preferred futures. They consider how data, information, systems, materials, tools and equipment (past and present) impact on our lives, and how these elements might be better designed and managed. Experimenting, drawing, modelling, designing and working with digital tools, equipment and software helps students to build their visual and spatial thinking and to create solutions, products, services and environments.
Personal and social capability
Across the Western Australian Curriculum, students develop personal and social capability as they learn to understand themselves and others, manage their relationships, lives, work and learning more effectively. The personal and social capability involves students in a range of practices including recognising and regulating emotions, developing empathy for and understanding of others, establishing positive relationships, making responsible decisions, working effectively in teams and handling challenging situations constructively.
Students develop personal and social capability as they engage in project management and development in a collaborative workspace. They direct their own learning, plan and carry out investigations, and become independent learners who can apply design thinking, technologies understanding and skills when making decisions. Students develop social and employability skills through working cooperatively in teams, sharing resources and processes, making group decisions, resolving conflict and showing leadership. Designing and innovation involve a degree of risk-taking and as students work with the uncertainty of sharing new ideas they develop resilience.
The Technologies learning area enhances students' personal and social capability by developing their social awareness. Students develop understanding of diversity by researching and identifying user needs. They consider past and present impacts of decisions on people, communities and environments and develop social responsibility through understanding of, empathy with and respect for others.
Ethical understanding
Across the Western Australian Curriculum, students develop ethical understanding as they identify and investigate ethical concepts, values, character traits and principles, and understand how reasoning can assist ethical judgement. Ethical understanding involves students in building a strong personal and socially oriented ethical outlook that helps them to manage context, conflict and uncertainty, and to develop an awareness of the influence that their values and behaviour have on others.
Students develop the capacity to understand and apply ethical and socially responsible principles when collaborating with others and creating, sharing and using technologies – materials, data, processes, tools and equipment. Using an ethical lens, they investigate past, current and future local, national, regional and global technological priorities. When engaged in systems thinking students evaluate their findings against the criteria of legality, environmental sustainability, economic viability, health, social and emotional responsibility and social awareness. They explore complex issues associated with technologies and consider possibilities. They are encouraged to develop informed values and attitudes.
Students learn about safe and ethical procedures for investigating and working with people, animals, data and materials. They consider the rights of others and their responsibilities in using sustainable practices that protect the planet and its life forms. They learn to appreciate and value the part they play in the social and natural systems in which they operate.
Students consider their own roles and responsibilities as discerning citizens, and learn to detect bias and inaccuracies. Understanding the protection of data, intellectual property and individual privacy in the school environment helps students to be ethical digital citizens.
Intercultural understanding
Across the Western Australian Curriculum, students develop intercultural understanding as they learn to value their own cultures, languages and beliefs, and those of others. They come to understand how personal, group and national identities are shaped, and the variable and changing nature of culture. The capability involves students in learning about and engaging with diverse cultures in ways that recognise commonalities and differences, create connections with others and cultivate mutual respect.
Students consider how technologies are used in diverse communities at local, national, regional and global levels, including their impact and potential to transform people's lives. They explore ways in which past and present practices enable people to use technologies to interact with one another across cultural boundaries. Students investigate how cultural identities and traditions influence the function and form of solutions, products, services and environments designed to meet the needs of daily life now and in the future.
In their interactions with others in online communities, students consider the dynamic and complex nature of cultures, including values, beliefs, practices and assumptions. They recognise and respond to the challenges of cultural diversity by applying appropriate social protocols. Students learn about the interactions between technologies and society and take responsibility for securing positive outcomes for members of all cultural groups including those faced with prejudice and misunderstanding.
Cross-Curriculum Priorities
The cross-curriculum priorities address the contemporary issues that students face in a globalised world. Teachers may find opportunities to incorporate the priorities into the teaching and learning program for Technologies. The cross-curriculum priorities are not assessed unless they are identified within the core content.
Aboriginal and Torres Strait Islander histories and cultures
In the Western Australian Curriculum: Technologies, the priority of Aboriginal and Torres Strait Islander histories and cultures may provide creative, engaging and diverse learning contexts for students to value and appreciate the contribution by the world's oldest continuous living cultures to past, present and emerging technologies.
In the Technologies learning area, students explore how Aboriginal and Torres Strait Islander Peoples' capacity for innovation is evident through the incorporation and application of a range of traditional, contemporary and emerging technologies and practices to purposefully build and/or maintain cultural, community and economic capacity. Students may apply this knowledge and understanding throughout the processes of observation, critical and creative thinking, action, experimentation and evaluation.
Asia and Australia's engagement with Asia
In the Western Australian Curriculum: Technologies, the priority of Asia and Australia's engagement with Asia provides diverse and authentic contexts to develop knowledge and understanding of technologies processes and production and related cultural, social and ethical issues. It enables students to recognise that interaction between human activity and the diverse environments of the Asia region continues to create the need for creative solutions and collaboration with others, including Australians, and has significance for the rest of the world.
Sustainability
In the Western Australian Curriculum: Technologies, the priority of sustainability provides authentic contexts for creating preferred futures. When students identify and critique a problem, need or opportunity; generate ideas or concepts; and create solutions, they give prime consideration to sustainability by anticipating and balancing economic, environmental and social impacts.
Technologies focuses on the knowledge, understanding and skills necessary to design for effective sustainability action. It recognises that actions are both individual and collective endeavours shared across local, regional and global communities and provides a basis for students to explore their own and competing viewpoints, values and interests. Understanding systems enables students to work with complexity, uncertainty and risk; make connections between disparate ideas and concepts; self-critique; and propose creative solutions that enhance sustainability.
Glossary
Design and Technologies
ABLEWA Stage A
ABLEWA A stage description
In Stage A, students are exposed to technologies, including its purpose and how technologies meet every day personal needs.
Students experience the characteristics and properties of some familiar designed solutions from one of the technologies contexts:
- Engineering principles and systems
- Food and fibre production
- Food specialisations
- Materials and technologies specialisations.
Students are exposed to designed solutions that meet their needs.
Knowledge and understanding
Technologies and society
Experience how people create familiar designed solutions to meet their needs (VCDSTS001)
Technologies contexts
Experience the characteristics and properties of familiar designed solutions in at least one technologies context (VCDSTC002)
Processes and production skills
Creating Designed Solutions
React to a designed solution that has been created and produced safely to meet their needs(VCDSCD003)
Achievement standard
By the end of Stage A, students react to significant designed solutions that meet their needs.
With guidance, students experience designed solutions in at least one technologies context. They begin to communicate their needs and indicate a choice or preference through accept and reject actions.
Students react to the use of tools and equipment and experience the sequenced steps involved in producing a designed solution.
ABLEWA Stage B
ABLEWA B stage description
In Stage B students explore technologies, including its purpose and how technologies meet personal and social needs.
Students examine the characteristics and properties of some technologies from one of the technologies contexts:
- Engineering principles and systems
- Food and fibre production
- Food specialisations
- Materials and technologies specialisations.
With teacher support, students communicate simple design ideas.
Students experience how designed solutions meet their needs.
Knowledge and understanding
Technologies and society
Explore the use of familiar designed solutions to meet their needs (VCDSTS004)
Technologies contexts
Explore the characteristics and properties of familiar designed solutions in at least one technologies context (VCDSTC005)
Processes and production skills
Creating Designed Solutions
Experience and explore how designed solutions are created and produced safely to meet personal needs(VCDSCD006)
Achievement standard
By the end of Stage B, students are using some familiar designed solutions appropriately to meet their needs.
With guidance, students explore designed solutions in at least one technologies context. They experience designed solution ideas and select materials and components based on personal preferences.
Students follow a design process step by step and use tools safely when prompted.
ABLEWA Stage C
ABLEWA C stage description
In Stage C students explore and investigate technologies, including its purpose and how technologies meet needs.
Students describe the characteristics and properties of familiar designed solutions from one of the technologies contexts:
- Engineering principles and systems
- Food and fibre production
- Food specialisations
- Materials and technologies specialisations.
With teacher support, students communicate simple design ideas. Students are introduced to different forms of evaluating designed solutions based on personal preferences.
Students, with teacher support, follow directions to complete their own or group design ideas or projects.
Knowledge and understanding
Technologies and society
Match familiar designed solutions to the personal needs they meet (VCDSTS007)
Technologies contexts
Examine and indicate the characteristics and properties of familiar designed solutions in at least two technologies contexts (VCDSTC008)
Processes and production skills
Creating Designed Solutions
Examine and indicate how designed solutions are created and produced safely to meet needs (VCDSCD009)
Achievement standard
By the end of Stage C, students use and identify the purpose of familiar designed solutions. They match some designed solutions to a need.
Students use designed solutions in at least two technologies contexts. With guidance, students reflect on created and produced designed solutions, developing ideas based on personal preferences. They begin to follow simple sequenced steps and teacher direction to use tools and equipment safely when producing designed solutions.
ABLEWA Stage D
ABLEWA D stage description
In Stage D students explore and investigate technologies, including its purpose and how technologies meet personal and social needs within local settings.
Students explore the characteristics and properties of familiar designed solutions from one of the technologies contexts:
- Engineering principles and systems
- Food and fibre production
- Food specialisations
- Materials and technologies specialisations.
With teacher support, students communicate simple design ideas and begin to evaluate designed solutions based on personal preferences.
Students begin to plan their design idea with teacher support, and follow simple steps and directions to complete their own or group design ideas or projects.
Knowledge and understanding
Technologies and society
Explore how people create familiar designed solutions and identify their ability to meet personal and local community needs (VCDSTS010)
Technologies contexts
Explore and communicate the characteristics and properties of familiar designed solutions in at least two technologies contexts (VCDSTC011)
Processes and production skills
Creating Designed Solutions
Explore and communicate how designed solutions are generated and produced to meet needs (VCDSCD012)
Achievement standard
By the end of Stage D, students describe the purpose of familiar designed solutions and what needs they meet.
Students use designed solutions in at least two technologies contexts, identifying significant features.
With guidance, students create designed solutions evaluating their ideas based on personal preferences. They select materials based on some understanding of their properties and characteristics. They follow simple sequenced steps to create a designed solution and demonstrate safe use of tools and equipment.
Pre-primary year Syllabus
The syllabus is based on the requirement that all students will study both Technologies subjects from Pre-primary to Year 8.
Year Level Description
Learning in Design and Technologies builds on the dispositions developed in the early years. Learning focuses on practical and applied knowledge and understanding of process and production skills.
In Pre-primary, students have hands on opportunities to explore designs and solutions in at least one of the following technologies contexts: Engineering principles and systems; Food and fibre production (includes Food specialisations in this year); and Materials and technologies specialisations. Students explore the design of products and begin to develop an understanding about products.
Students have opportunities to explore technologies taking particular note of the components and equipment used to make products. They begin to develop an understanding that products have a purpose for their own personal needs and that of their family. Students reflect on designed solutions using questions such as 'How does it work?', 'What purpose does it meet?', 'Who will use it?', 'What do I like about it?' or 'How can it be improved?'
Pre-primary students begin to explore the needs for design of products that impact on people's everyday lives. Using a range of techniques, students will communicate their design ideas.
Knowledge and understanding
Technologies and society
People produce familiar products to meet personal and community needs (ACTDEK001)
Technologies contexts
Engineering principles and systems
Ways in which objects move: push, pull, bounce, slide, fall, spin, float (ACTDEK002)
Food and fibre production
Plant and animal products are used in everyday life for food, clothing and shelter (ACTDEK003)
Materials and technologies specialisations
Characteristics of materials can be explored using senses (ACTDEK004)
Processes and production skills
Creating solutions by:
Investigating and defining
Explore needs for design (WATPPS01)
Designing
Generate and record design ideas through describing, drawing, modelling and/or a sequence of written or spoken steps (WATPPS02)
Producing and implementing
Use given components and equipment to safely make simple solutions (WATPPS03)
Evaluating
Use personal preferences to evaluate the success of simple solutions (WATPPS04)
Collaborating and managing
Work independently, or with others when required, for solutions (WATPPS05)
Achievement standard
At Standard, students identify people that produce familiar objects within the community and some simple stages of the production process. In Engineering principles and systems, students move objects in a range of ways and observe their reactions. In Food and fibre production, students connect plant and animal products to their use as food, clothing and/or shelter. In Materials and technologies specialisations, students explore and select materials to use for construction, considering the materials’ characteristics.
With all Design and Technology contexts, students explore needs for designing simple solutions. They generate and record design ideas through describing, drawing, modelling and/or a sequence of written or spoken steps. Students safely use given components and equipment, to make simple solutions and evaluate their success using personal preferences.
Year 1 Syllabus
The syllabus is based on the requirement that all students will study both Technologies subjects from Pre-primary to Year 8.
Year Level Description
Learning in Design and Technologies builds on the dispositions developed in the early years. Learning focuses on practical and applied knowledge and understanding of process and production skills.
In Year 1, students have opportunities to create solutions in one of the following technologies contexts: Engineering principles and systems; Food and fibre production (includes Food specialisations in this year); and Materials and technologies specialisations. Students investigate the process of designing and producing products and services.
Students have opportunities to explore and question the use of technologies including components and equipment, their purpose and how they meet personal and social needs within known settings. They develop an understanding of how communities and local circumstances influence design and technologies decisions. Students appraise designed solutions using questions such as 'How does it work?', 'What purpose does it meet?', 'Who will use it?', 'What do I like about it?' or 'How can it be improved?'
Students begin to consider the impact of design decisions and the use of technologies on others in their local community. They have opportunities to reflect on their participation in a design process. With support, students develop new strategies, and engage in different ways of evaluating and judging products and services based on personal preferences. Students are encouraged to make informed choices and to accept challenges, take risks and manage change when unexpected outcomes occur.
Using a range of techniques, including a variety of graphical representations to communicate, students draw, model and explain design ideas; label drawings; draw products and simple environments; and verbalise design ideas.
Knowledge and understanding
Technologies and society
People produce familiar products and services to meet personal and community needs (ACTDEK001)
Technologies contexts
Engineering principles and systems
Ways objects can be moved using technology (ACTDEK002)
Food and fibre production
Plants and animals used for production have basic needs, such as food/nutrients, water, space, protection (ACTDEK003)
Materials and technologies specialisations
Characteristics and behaviours of individual materials used in products (ACTDEK004)
Processes and production skills
Creating solutions by:
Investigating and defining
Explore opportunities for design (WATPPS06)
Designing
Develop and communicate design ideas through describing, drawing, modelling and/or a sequence of written or spoken steps (WATPPS07)
Producing and implementing
Use given components and equipment to safely make solutions (WATPPS08)
Evaluating
Use personal preferences to evaluate the success of design processes (WATPPS09)
Collaborating and managing
Works independently, or with others when required, to safely create and share sequenced steps for solutions (WATPPS10)
Achievement standard
At Standard, students identify people that produce familiar products and services and recall some simple stages of the production process. In Engineering principles and systems, students use technology to move objects and observe the reactions. In Food and fibre production, students identify plants and animals used for production and their basic needs. In Materials and technologies specialisations, students observe, explore and select materials to use for construction based on materials’ characteristics and behaviours.
With all Design and Technology contexts, students explore opportunities when designing products or solutions. They develop and communicate design ideas through describing, drawing, modelling and/or a sequence of written or spoken steps. Students use given components and equipment and work safely to make solutions. They develop personal preferences to evaluate the success of design processes. Students work independently, or with others, to safely create and share sequenced steps for solutions.
Year 2 Syllabus
The syllabus is based on the requirement that all students will study both Technologies subjects from Pre-primary to Year 8.
Year Level Description
Learning in Design and Technologies builds on the dispositions developed in the early years. Learning focuses on practical and applied knowledge and understanding of process and production skills.
In Year 2, students have opportunities to create solutions in at least one of the following technologies contexts: Engineering principles and systems; Food and fibre production (includes Food specialisations in this year); and Materials and technologies specialisations. Students experience designing and producing products, services and environments.
Students have opportunities to investigate technologies: materials, systems, components, tools and equipment, including their purpose and how they meet personal and social needs within local settings. They develop an understanding of how society and environmental sustainability factors influence design and technologies decisions. Students evaluate and judge designed solutions using questions such as 'How does it work?', 'What purpose does it meet?', 'Who will use it?', 'What do I like about it?' or 'How can it be improved?' They are encouraged to make judgments about the design solutions in order to solve problems in their own design ideas.
Students begin to consider the impact of their decisions, and of technologies, on others and the environment, including in relation to preferred futures. They have opportunities to reflect on their participation in a design process. With support, students develop new strategies and engage in different ways of evaluating and judging products, services and environments based on personal preferences.
Using a range of techniques, including a variety of graphical representations to communicate, students draw, model and explain design ideas; label drawings; draw products and simple environments; and verbalise design ideas.
Knowledge and understanding
Technologies and society
People design and produce familiar products, services and environments to meet local and community needs (ACTDEK001)
Technologies contexts
Engineering principles and systems
Forces create movement in objects (ACTDEK002)
Food and fibre production
Food and fibre choices for healthy living (ACTDEK003)
Materials and technologies specialisations
Characteristics and properties of materials and individual components that are used to produce design solutions (ACTDEK004)
Processes and production skills
Creating solutions by:
Investigating and defining
Explore design to meet needs or opportunities (WATPPS11)
Designing
Develop, communicate and discuss design ideas through describing, drawing, modelling and/or a sequence of steps (WATPPS12)
Producing and implementing
Use components and given equipment to safely make solutions (WATPPS13)
Evaluating
Use simple criteria to evaluate the success of design processes and solutions (WATPPS14)
Collaborating and managing
Work independently, or collaboratively when required, to organise information and ideas to safely create and share sequenced steps for solutions (WATPPS15)
Achievement standard
At Standard, students identify and exemplify roles of people that design and produce products, services and environments within the community. In Engineering principles and systems, students use a range of forces to move objects and observe the reactions. In Food and fibre production, students make simple connections between healthy living, food and fibre choices. In Materials and technologies specialisations, students develop ideas and make design decisions, considering both the characteristics and properties of materials.
With all Design and Technology contexts, students explore design to meet needs or opportunities. They develop, communicate and discuss design ideas through describing, drawing, modelling and/or sequenced steps. Students use components and given equipment to safely make solutions. They use simple criteria to evaluate the success of design processes and solutions. Students work independently, or collaboratively, to organise information and ideas to safely create and share sequenced steps for solutions.
Year 3 Syllabus
The syllabus is based on the requirement that all students will study both Technologies subjects from Pre-primary to Year 8.
Year Level Description
Learning in Design and Technologies builds on the range of concepts, skills and processes developed in previous years.
In Year 3, students have opportunities to learn about technologies in society as they create solutions in at least one of the following technologies contexts: Engineering principles and systems; Food and fibre production (includes Food specialisations in this year); and Materials and technologies specialisations. Students are provided with opportunities to produce products and develop an understanding that designs for services and environments meet community needs.
Students have opportunities to develop self-ownership of their ideas. They explore creative, innovative and imaginative ideas and approaches to achieve solutions. Students begin thinking about their peers, their communities and themselves as consumers, and explore the need for services and environments within both the local and broader community.
Students plan with an awareness of the characteristics and properties of materials, and the use of tools and equipment. They have opportunities to reflect on their actions, and develop decision-making skills. Students explore aspects of the social implications of existing products and processes to develop an understanding of their place in the world.
Students communicate using a range of techniques for documenting design and production ideas.
Knowledge and understanding
Technologies and society
Role of people in design and technologies occupations (ACTDEK010)
Ways products, services and environments are designed to meet community needs (ACTDEK010)
Technologies contexts
Engineering principles and systems
Forces, and the properties of materials, affect the behaviour of objects (ACTDEK011)
Food and fibre production
Types of food and fibre produced in different environments, cultures or time periods, including the equipment used to produce or prepare them (ACTDEK012)
Materials and technologies specialisations
Suitability and safe practice when using materials, tools and equipment for a range of purposes (ACTDEK013)
Processes and production skills
Creating solutions by:
Investigating and defining
Create a sequence of steps to solve a given task (WATPPS16)
Designing
Develop and communicate ideas using labelled drawings and appropriate technical terms (WATPPS17)
Producing and implementing
Select, and safely use, appropriate components with given equipment to make a solution (WATPPS18)
Evaluating
Use criteria to evaluate design processes and solutions developed (WATPPS19)
Collaborating and managing
Work independently, or collaboratively when required, to plan, safely create and communicate sequenced steps (WATPPS20)
Achievement standard
At Standard, students identify roles people in design and technology have in the community and explore design development processes of products, services and environments. In Engineering principles and systems, students observe and recognise ways applied forces and properties of materials affect the behaviour of objects. In Food and fibre production, students identify equipment and simple processes used in food and fibre production from a range of environments, cultures or time periods. In Materials and technologies specialisations, students select and safely use suitable materials, tools and equipment to create design solutions.
With all Design and Technology contexts, students create a sequence of steps to solve a given task. They develop and communicate ideas using labelled drawings and appropriate technical terms. Students select and safely use appropriate components with given equipment to make a solution. They use criteria to evaluate design processes and solutions developed. Students work independently, or collaboratively to plan, safely create and communicate sequenced steps.
Year 4 Syllabus
The syllabus is based on the requirement that all students will study both Technologies subjects from Pre-primary to Year 8.
Year Level Description
Learning in Design and Technologies builds on the range of concepts, skills and processes developed in previous years.
In Year 4, students have opportunities to learn about technologies in society as they create solutions in at least one of the following technologies contexts: Engineering principles and systems; Food and fibre production (includes Food specialisations in this year); and Materials and technologies specialisations. Students are provided with opportunities to design and produce products, services and sustainable environments.
Students' sense of ownership of their ideas is further developed and expanded, with a greater focus on community needs when making decisions about designs. They have opportunities to develop a broader understanding of the concept of themselves as consumers. Students begin to explore and learn to harness their creative, innovative and imaginative ideas.
Students become aware of the design characteristics and properties of materials, and the use of components and equipment when planning solutions. They have opportunities to reflect on actions to refine design solutions through the use of decision-making skills. Students engage in learning to explore the social and environmental sustainability implications of existing products and processes to raise awareness of their place in the world. Students explore the role of those working in design and technologies occupations, and how they think about the way a product might change in the future.
Students broaden the techniques they use to clarify and present ideas, such as drawing annotated diagrams for documenting design and production ideas.
Knowledge and understanding
Technologies and society
Role of people in design and technologies occupations (ACTDEK010)
Ways products, services and environments are designed to meet community needs, including consideration of sustainability (ACTDEK010)
Technologies contexts
Engineering principles and systems
Forces, and the properties of materials, affect the behaviour of a product or system (ACTDEK011)
Food and fibre production
Types of technologies used in food and fibre production or processing, including how they are used to help meet consumer needs (ACTDEK012)
Materials and technologies specialisations
Suitability and safe practice when using materials, systems and components for a range of purposes (ACTDEK013)
Processes and production skills
Creating solutions by:
Investigating and defining
Define a sequence of steps to design a solution for a given task (WATPPS21)
Identify and choose the appropriate resources from a given set (WATPPS22)
Designing
Develop and communicate design ideas and decisions using annotated drawings and appropriate technical terms (WATPPS23)
Producing and implementing
Select, and safely use, appropriate components and equipment to make solutions (WATPPS24)
Evaluating
Use criteria to evaluate and justify simple design processes and solutions (WATPPS25)
Collaborating and managing
Work independently, or collaboratively when required, to plan, safely create and communicate ideas and information for solutions (WATPPS26)
Achievement standard
At Standard, students identify roles people in design and technologies occupations have in the community and ways that products, services and environments are designed and produced to meet community needs, considering sustainability. In Engineering principles and systems, students recognise ways forces and properties of materials, affect the behaviour of a product or system. In Food and fibre production, students identify consumer needs and how technology is used in food and natural fibre production or processing. In Materials and technologies specialisations, students implement safe practices and select suitable materials, systems and components for a range of purposes.
With all Design and Technology contexts, students use sequenced steps to design a solution for a given task. They identify and choose the appropriate resources from a given set. Students develop and communicate design ideas and decisions, using annotated drawings and appropriate technical terms. They select and safely use appropriate components and equipment to make solutions. Students use criteria to evaluate and justify simple design processes and solutions for a given task. They work independently, or collaboratively, to plan, safely create and communicate ideas and information for solutions.
Year 5 Syllabus
The syllabus is based on the requirement that all students will study both Technologies subjects from Pre-primary to Year 8.
Year Level Description
Learning in Design and Technologies builds on the range of concepts, skills and processes developed in previous years.
In Year 5, students have opportunities to learn about technologies in society through different technology contexts as they create solutions in at least one of the following technologies contexts: Engineering principles and systems; Food and fibre production; Food specialisations; and Materials and technologies specialisations. Students are provided with opportunities to produce products and develop an understanding that designs for services and environments meet community needs.
Students have opportunities to explore technologies that incorporate materials, components, and equipment used in the home and wider community. They continue to consider society, cultural needs and environmental factors, paying attention to sustainable practices. Students question why and for whom technologies are developed.
Students begin to engage with ideas beyond the familiar, exploring how the people working in a range of technologies contexts contribute to society. They are provided with opportunities to explore innovative design solutions that build on their own design capabilities.
Using a range of techniques, students explore how to represent objects and ideas in a variety of forms, such as thumbnail sketches, models, drawings, diagrams and storyboards to communicate the development of designed solutions.
Knowledge and understanding
Technologies and society
How people address competing considerations when designing products, services and environments (ACTDEK019)
Technologies contexts
Engineering principles and systems
Forces can control movement, sound or light in a product or system (ACTDEK020)
Food and fibre production
People in design and technologies occupations aim to increase efficiency of production systems, or consumer satisfaction of food and natural fibre products (ACTDEK021)
Food specialisations
Food safety and hygiene practices (ACTDEK022)
Materials and technologies specialisations
Characteristics and properties of a range of materials and components, and the suitability and safe practice of their use (ACTDEK023)
Processes and production skills
Creating solutions by:
Investigating and defining
Define a problem, and set of sequenced steps, with users making a decision to create a solution for a given task (WATPPS27)
Identify available resources (WATPPS28)
Designing
Develop and communicate alternative solutions, and follow design ideas, using annotated diagrams, storyboards and appropriate technical terms (WATPPS29)
Producing and implementing
Select, and apply, safe procedures when using components and equipment to make solutions (WATPPS30)
Evaluating
Develop negotiated criteria to evaluate and justify design processes and solutions (WATPPS31)
Collaborating and managing
Work independently, or collaboratively when required, to plan, safely develop and communicate ideas and information for solutions (WATPPS32)
Achievement standard
At Standard, students identify ways people address and overcome competing considerations when designing products, services and environments. In Engineering principles and systems, students distinguish various ways forces control movement, sound or light in a product or system. In Food and fibre production, students identify ways people in design and technology occupations aim to increase the efficiency of production systems or consumer satisfaction of food and natural fibre products. In Food specialisations, students identify and implement a variety of food and hygiene practices. In Materials and technologies specialisations, students outline and apply suitable and safe practices and are able to classify the characteristics and properties of a range of materials and components.
With all Design and Technology contexts, students define a problem, identify available resources and create sequenced steps to assist in decision making for a given task. They develop and communicate alternative solutions, and use annotated diagrams, storyboards and appropriate technical terms when following design ideas. Students select and apply safe procedures when using components and equipment. They develop negotiated criteria to evaluate and justify design processes and solutions. Students work independently, or collaboratively, to plan, safely develop and communicate ideas and information.
Year 6 Syllabus
The syllabus is based on the requirement that all students will study both Technologies subjects from Pre-primary to Year 8.
Year Level Description
Learning in Design and Technologies builds on the range of concepts, skills and processes developed in previous years.
In Year 6, students have opportunities to learn about technologies in society through different technology contexts as they create solutions in at least one of the following technologies contexts: Engineering principles and systems; Food and fibre production; Food specialisations; and Materials and technologies specialisations. Students are provided with opportunities to produce products and develop an understanding that designs for services and environments meet community needs.
Students have the opportunity to begin to critically examine technologies, including materials, systems, components, tools and equipment that are used regularly in the home and wider community. They explore and begin to consider ethical points of view, social impact and environmentally sustainable factors when developing design solutions. Students examine why and for whom technologies are developed.
Students have opportunities to engage with ideas beyond the familiar, exploring how people working in a range of technologies contexts contribute to society. They continue to build on design capabilities through broadening their own design ideas used in solutions. Students have opportunities to explore trends and data to predict what the future will be like, and suggest design decisions that contribute positively to preferred futures.
Using technologies to suit the purpose, students explore how to represent objects and ideas in a variety of forms to communicate the development of designed solutions. They use a range of preferred techniques to illustrate how products function.
Knowledge and understanding
Technologies and society
How people address competing considerations, including sustainability when designing products, services and environments for current and future use (ACTDEK019)
Technologies contexts
Engineering principles and systems
Electrical energy and forces can control movement, sound or light in a product or system (ACTDEK020)
Food and fibre production
Past performance, and current and future needs are considered when designing sustainable food and fibre systems for products (ACTDEK021)
Food specialisations
Principles of food preparation for healthy eating (ACTDEK022)
Materials and technologies specialisations
Characteristics, properties and safe practice of a range of materials, systems, tools and equipment; and evaluate the suitability of their use (ACTDEK023)
Processes and production skills
Creating solutions by:
Investigating and defining
Define a problem, and a set of sequenced steps, with users making decisions to create a solution for a given task (WATPPS33)
Identify available resources (WATPPS34)
Designing
Design, modify, follow and represent both diagrammatically, and in written text, alternative solutions using a range of techniques, appropriate technical terms and technology (WATPPS35)
Producing and implementing
Select, and apply, safe procedures when using a variety of components and equipment to make solutions (WATPPS36)
Evaluating
Develop collaborative criteria to evaluate and justify design processes and solutions (WATPPS37)
Collaborating and managing
Work independently, or collaboratively when required, considering resources and safety, to plan, develop and communicate ideas and information for solutions (WATPPS38)
Achievement standard
At Standard, students identify how people address and overcome competing considerations, including sustainability, when designing products, services and environments for current and future use. In Engineering principles and systems, students connect ways electrical energy and forces can control movement, sound or light in a product or system. In Food and fibre production, students investigate and determine what past, current and future needs are to be considered when designing sustainable food and natural fibre systems for products. In Food specialisations, students identify and consider principles of food preparation and benefits of healthy eating. In Materials and technologies specialisations, students consider suitability of use when defining characteristics, properties and safe handling practices of a range of materials, systems, tools and equipment.
With all Design and Technology contexts, students identify available resources to design a solution for a given task, outlining problem-solving decisions, using sequenced steps. Students develop alternative solutions by designing, modifying and following both diagrammatically and in written text, using a range of appropriate technical terms, technologies and techniques. They select and apply safe procedures when using a variety of components and equipment to make solutions. Students develop criteria collaboratively to evaluate and justify design processes and solutions. They work independently, or collaboratively, considering resources and safety to plan, develop and communicate ideas and information for solutions.
Year 7 Syllabus
The syllabus is based on the requirement that all students will study both Technologies subjects from Pre-primary to Year 8.
Year Level Description
Learning in Design and Technologies builds on concepts, skills and processes developed in earlier years, and teachers will revisit, strengthen and extend these as needed.
In Year 7, students have opportunities to learn about technologies in society at least once in the following technologies contexts: Engineering principles and systems; Food and fibre production; Food specialisations; and Materials and technologies specialisations. Students are provided with opportunities to design and produce products, services and environments.
Students have opportunities to select from a range of technologies, materials, components, tools and equipment. They consider the ways characteristics and properties of technologies can be combined to design and produce sustainable solutions. They develop strategies which enable them to consider society and ethics; social, ethical and sustainability factors. Students' use of creativity, innovation and enterprise skills is encouraged to increase independence and collaboration.
Students are given opportunities to respond to feedback from others and evaluate their design processes and solutions. They investigate design and technology solutions and the implications for each on society, locally, regionally and globally. Students develop their techniques for evaluating the advantages and disadvantages of design ideas.
Students have opportunities to engage with a range of technologies, including a variety of graphical representation techniques to communicate ideas. Students generate and clarify ideas through sketching, modelling and perspective drawings.
Students identify the increasingly complex sequences and steps involved in design tasks. They develop plans to manage design tasks, including safe and responsible use of materials and tools to successfully complete design tasks.
Knowledge and understanding
Technologies and society
Competing factors, including social, ethical and sustainability considerations, in the development of technologies (ACTDEK029)
Ways in which products, services and environments evolve locally, regionally and globally (ACTDEK030)
Technologies contexts
Engineering principles and systems
The use of motion, force and energy to manipulate and control electromechanical and mechanical systems (ACTDEK031)
Food and fibre production
Production systems for food and fibre or their products, including key features of their design (ACTDEK032)
Food specialisations
Nutritional value and physical properties of food determine preparation techniques and presentation (ACTDEK033)
Materials and technologies specialisations
Material and technology decisions and processes influence the selection and combination of materials, systems, components, tools and equipment (ACTDEK034)
Processes and production skills
Creating solutions by:
Investigating and defining
Define and break down a given task, identifying the purpose (WATPPS39)
Consider components/resources to develop solutions, identifying constraints (WATPPS40)
Designing
Design, develop, review and communicate design ideas, plans and processes within a given context, using a range of techniques, appropriate technical terms and technology (WATPPS41)
Follow a plan designed to solve a problem, using a sequence of steps (WATPPS42)
Producing and implementing
Safely make solutions using a range of components, equipment and techniques (WATPPS43)
Evaluating
Independently apply given contextual criteria to evaluate design processes and solutions (WATPPS44)
Collaborating and managing
Work independently, and collaboratively when required, to plan, develop and communicate ideas and information, using management processes (WATPPS45)
Achievement standard
At Standard, students outline ways in which products, services and environments evolve locally, regionally and globally and recognise competing factors, including social, ethical and sustainability in the development of technologies. In Engineering principles and systems, students identify the use of motion, force and energy to manipulate and to control electromechanical and mechanical systems. In Food and fibre production, students identify components of food and fibre production systems including key features of their design. In Food specialisations, students identify nutritional values and physical properties of food to determine preparation techniques and presentation. In Materials and technologies specialisations, students identify how the selection of material and technology process is influenced by the combination of materials, systems, components, tools and equipment.
With all Design and Technology contexts, students develop solutions and identify the purpose for a given task by considering constraints and components/resources. Students use a range of techniques, appropriate technical terms and technologies to design, develop, review and communicate design ideas, plans and processes. They follow sequenced steps to a problem-solving plan. Students apply safe procedures to make solutions, using a range of components, equipment and techniques. They apply given contextual criteria to independently evaluate design processes and solutions. Students work independently, and collaboratively, to plan, develop and communicate ideas and information, when using management processes.
Year 8 Syllabus
The syllabus is based on the requirement that all students will study both Technologies subjects from Pre-primary to Year 8.
Year Level Description
Learning in Design and Technologies builds on concepts, skills and processes developed in earlier years, and teachers will revisit, strengthen and extend them as needed.
In Year 8, students have opportunities to learn about technologies in society at least once in the following technologies contexts: Engineering principles and systems; Food and fibre production; Food specialisations; and Materials and technologies specialisations. Students are provided with opportunities to design and produce products, services and environments.
Students have opportunities to investigate and select from a range of technologies, materials, systems, components, tools and equipment. They consider the ways characteristics and properties of technologies can be combined to produce sustainable solutions. Considering society and ethics; and economic, environmental and social sustainability factors is of increasing importance in this year. Students use creativity, innovation and enterprise skills with increasing independence and collaboration.
Students have the opportunity to respond to feedback from others and evaluate their design processes and solutions. They investigate design and technology professions and the contributions that each makes to society through creativity, innovation and enterprise. Students are expected to evaluate the advantages and disadvantages of design ideas and technologies.
Students have the opportunity to engage with a range of technologies, including a variety of graphical representation techniques, to generate and clarify ideas through annotated sketches, modelling and scaled drawings.
Students identify the sequences and steps involved in design tasks. They have opportunities to develop plans to manage design tasks, including safe and responsible use of materials and tools, and apply management plans to successfully complete design tasks. Students establish safety procedures that minimise risk and manage a project with consideration to safety and efficiency, when making solutions.
Knowledge and understanding
Technologies and society
Social, ethical and sustainability considerations, in the development of technologies and designed solutions, to meet community needs for economic, environmental and social sustainability (ACTDEK029)
Development of products, services and environments through the creativity, innovation and enterprise of individuals and groups (ACTDEK030)
Technologies contexts
Engineering principles and systems
The design of simple solutions using motion, force and energy, to manipulate and control electromechanical and mechanical systems (ACTDEK031)
Food and fibre production
Sustainable production systems are subject to competing demands (social, environmental, economic) and how these factors influence their design (ACTDEK032)
Food specialisations
Sensory properties of food to create healthy eating solutions (ACTDEK033)
Materials and technologies specialisations
The process for the selection and combination of materials, systems, components, tools and equipment (ACTDEK034)
Processes and production skills
Creating solutions by:
Investigating and defining
Investigate a given need or opportunity for a specific purpose (WATPPS46)
Evaluate and apply a given brief (WATPPS47)
Consider components/resources to develop solutions, identifying constraints (WATPPS48)
Designing
Design, develop, evaluate and communicate alternative solutions, using appropriate technical terms and technology (WATPPS49)
Produce a simple plan designed to solve a problem, using a sequence of steps (WATPPS50)
Producing and implementing
Safely apply appropriate techniques to make solutions using a range of components and equipment (WATPPS51)
Evaluating
Develop contextual criteria independently to assess design processes and solutions (WATPPS52)
Collaborating and managing
Work independently, and collaboratively when required, to plan, develop and communicate ideas and information when managing projects (WATPPS53)
Achievement standard
At Standard, students outline the creativity, innovation and enterprise of individuals and groups that develop products, services and environments. They consider social, ethical and sustainability factors in the design and development of technologies. In Engineering principles and systems, students identify and use the design of simple solutions using motion, force and energy, to manipulate and control electromechanical and mechanical systems. In Food and fibre production, students provide information on how competing social, environmental and economic demands influence the design of sustainable food and fibre production systems. In Food specialisations, students explore and identify sensory properties of foods used in creating healthy eating solutions. In Materials and technologies specialisations, students identify decision making demands of selecting and combining materials, systems, components, tools and equipment.
With all Design and Technology contexts, students investigate a given need or opportunity for a specific purpose. They evaluate and apply a given design brief, using some examples. Students consider and select components/resources to develop solutions, identifying constraints. They use appropriate technical terms and technology to design, develop, evaluate and communicate alternative design solutions. Students develop sequenced steps to produce a simple, problem-solving plan. They apply safe and appropriate techniques to make solutions, using a range of components and equipment. Students independently develop contextual criteria to assess design processes and solutions. They work independently, and collaboratively, to plan, develop and communicate ideas and information when managing projects.
Year 9 Syllabus
The syllabus is based on the requirement that in Years 9 and 10 the study of Technologies is optional.
Year Level Description
Learning in Design and Technologies builds on concepts, skills and processes developed in earlier years, and teachers will revisit, strengthen and extend them as needed.
In Year 9, students have opportunities to learn about technologies in society at least once in the following technologies contexts: Engineering principles and systems; Food and fibre production; Food specialisations; and Materials and technologies specialisations. Students are provided with opportunities to design and produce products, services and environments.
Students have opportunities to use design and technologies knowledge and understanding, processes and production skills, and design thinking to produce solutions to identified needs or opportunities. They work independently and collaboratively. Students specifically focus on solutions, taking into account social values; economic, environmental and social sustainability factors. They have the opportunity to use creativity, innovation and enterprise skills with increasing confidence, independence and collaboration.
Using a range of increasingly
sophisticated technologies, including a variety of graphical representation
techniques,
students have opportunities to generate and represent original ideas and
production plans in
two-dimensional and three-dimensional representations.
Students identify and establish safety procedures that minimise risk and manage projects. They learn to transfer theoretical knowledge to practical activities.
Knowledge and understanding
Technologies and society
Social, ethical and sustainability considerations that impact on designed solutions (ACTDEK040)
Development of products, services and environments, with consideration of economic, environmental and social sustainability (ACTDEK041)
Technologies contexts
Engineering principles and systems
The characteristics and properties of materials, combined with force, motion and energy, to create solutions (ACTDEK043)
Food and fibre production
Food and fibre production and/or marketing, and the generation of sustainable solutions (ACTDEK044)
Food specialisations
Principles of food including safety, nutrition, preservation, preparation, presentation, physical and sensory properties and perceptions (ACTDEK045)
Materials and technologies specialisations
Characteristics and properties of materials, systems, components, tools and equipment used to create designed solutions (ACTDEK046)
Technologies can be combined and used to create designed solutions (ACTDEK047)
Processes and production skills
Creating solutions by:
Investigating and defining
Identify and define the needs of a stakeholder, to create a brief, for a solution (WATPPS54)
Investigate a selection of components/resources to develop solution ideas, identifying and considering constraints (WATPPS55)
Designing
Apply design thinking, creativity and enterprise skills (WATPPS56)
Design solutions assessing alternative designs against given criteria, using appropriate technical terms and technology (WATPPS57)
Producing and implementing
Select, and safely implement and test appropriate technologies and processes, to make solutions (WATPPS58)
Evaluating
Evaluate design processes and solutions against student-developed criteria (WATPPS59)
Collaborating and managing
Work independently, and collaboratively to manage projects, using digital technology and an iterative and collaborative approach. Considers time, cost, risk and safety (WATPPS60)
Achievement standard
At Standard, students identify social, ethical and sustainability factors and consider economic, environmental and social sustainability in the development of designed solutions for products, services and environments. In Engineering principles and systems, students create solutions through identifying characteristics and properties of materials and the influencing factors of force, motion and energy. In Food and fibre production, students consider the effect of food and fibre production and/or marketing influences, and considers the generation of sustainable solutions. In Food specialisations, students describe the principles of food safety, nutrition, preparation, presentation, preservation, physical and sensory properties and perceptions. In Materials and technologies specialisations, students identify characteristics and properties of materials, systems, components, tools and equipment and outline how technologies can be combined and used to create designed solutions.
With all Design and Technology contexts, students identify and define the needs of a stakeholder to create a design brief for a solution. They investigate a selection of components/resources to develop ideas, identifying and considering constraints. Students apply design thinking, creativity and enterprise skills. They provide design solutions assessing alternative designs against given criteria, using appropriate technical terms and technology. Students select, test and safely implement appropriate technologies and processes to make solutions. They evaluate design processes and solutions against student-developed criteria. Students work independently and collaboratively to manage projects, using digital technology and an iterative and collaborative approach. They consider time, cost, risk and safety.
Year 10 Syllabus
The syllabus is based on the requirement that in Years 9 and 10 the study of Technologies is optional.
Year Level Description
Learning in Design and Technologies builds on concepts, skills and processes developed in earlier years, and teachers will revisit, strengthen and extend them as needed.
In Year 10, students have opportunities to learn about technologies in society at least once in the following technologies contexts: Engineering principles and systems; Food and fibre production; Food specialisations; and Materials and technologies specialisations. Students are provided with opportunities to design and produce products, services and environments.
Students have opportunities to use design and technologies knowledge and understanding, processes and production skills, and design thinking, to produce solutions to identified needs or opportunities. Students work independently and collaboratively. They have opportunities to understand the complex interdependencies involved in the development of technologies and enterprises. The focus is on students designing solutions, taking into account ethics; legal issues; social values; economic, environmental and social sustainability factors; and using more sophisticated strategies. They use creativity, innovation and enterprise skills with confidence, independence and collaboration.
Using a range of technologies, including a variety of graphical representation techniques, students have opportunities to generate and represent original ideas and production plans in two-dimensional and three-dimensional representations using a range of technical drawings, including perspective, scale, orthogonal and production drawings with sectional and exploded views, appropriate to their designs.
Students identify the steps involved in planning the production of designed solutions. They develop detailed project management plans incorporating elements, such as sequenced time, cost and action plans to manage a range of design tasks safely. Students apply management plans, changing direction when necessary, to successfully complete design tasks. They continue to identify and establish safety procedures that minimise risk and manage projects maintaining safety standards and management procedures to ensure success. Learning experiences require students to transfer theoretical knowledge to practical activities across a range of projects.
Knowledge and understanding
Technologies and society
Social, ethical and sustainability considerations that impact on designed solutions, complexity of design, and production processes involved (ACTDEK040)
Impact of emerging technologies on design decisions, and/or economic, environmental and social sustainability (ACTDEK041)
Technologies contexts
Engineering principles and systems
The process of materials being combined with force, motion and energy to create solutions (ACTDEK043)
Food and fibre production
The role of emerging research and technology in the design of ethical and sustainable products (ACTDEK044)
Food specialisations
Healthy eating through the skills and knowledge of nutrients and the application of the principles of food safety, preservation, preparation, presentation and sensory perceptions (ACTDEK045)
Materials and technologies specialisations
The combination of a range of characteristics and properties of materials, systems, components, tools and equipment to create designed solutions (ACTDEK046)
Designed solutions within a range of technologies specialisations, using combined technologies (ACTDEK047)
Processes and production skills
Creating solutions by:
Investigating and defining
Identify the needs of the client/stakeholder to determine the basis for a solution (WATPPS61)
Create and critique briefs to solutions (WATPPS62)
Investigate components/resources to develop increasingly sophisticated solutions, identifying and considering associated constraints (WATPPS63)
Designing
Apply design thinking, creativity, enterprise skills and innovation to develop, modify and communicate design ideas of increasing sophistication (WATPPS64)
Design possible solutions, analysing designs against criteria, including functionality, accessibility, usability and aesthetics, using appropriate technical terms and technology (WATPPS65)
Producing and implementing
Select, justify, and safely implement and test appropriate technologies and processes, to make solutions (WATPPS66)
Evaluating
Analyse design processes and solutions against student-developed criteria (WATPPS67)
Collaborating and managing
Work independently, and collaboratively to manage projects, using digital technology and an iterative and collaborative approach. Considers time, cost, risk, safety, production processes, sustainability and legal responsibilities (WATPPS68)
Achievement standard
At Standard, students consider social, ethical and sustainability factors that impact on designed solutions, complexity of design, and production processes. They outline how design decisions, and/or economic, environmental and social sustainability is influenced by emerging technologies. In Engineering principles and systems, students identify the process of combining of materials with force, motion and energy to create solutions. In Food and fibre production, students outline the role emerging research and technology has on the design of ethical and sustainable food and fibre products. In Food specialisations, students identify ways to prepare and present foods for healthy eating using processing skills and techniques, applying knowledge of nutrients, principles of food safety, preparation, presentation, preservation, physical and sensory properties and perceptions. In Materials and technologies specialisations, students combine a range of characteristics and properties of materials, systems, components, tools, technologies and equipment to create designed solutions.
With all Design and Technology contexts, students identify the needs of the client/stakeholder to determine the basis for a solution. They create and critique design briefs. Students investigate components/resources to develop increasingly sophisticated solutions, identifying and considering associated constraints. They apply design thinking, creativity, enterprise skills and innovation to develop, modify and communicate design ideas of increasing sophistication. Students design possible solutions, analysing designs against criteria, including functionality, accessibility, usability and aesthetics, using appropriate technical terms and technology. They select, justify and safely implement and test appropriate technologies and processes to make solutions. Students provide relevant analysis of design processes and solutions against student-developed criteria. They work independently, and collaboratively to manage projects, using digital technology and an iterative and collaborative approach. Students consider time, cost, risk, safety, production processes, sustainability and legal responsibilities.