Ways of Teaching
The 'ways of teaching' aims to support teachers with planning for curriculum delivery across the phases of learning.
The 'ways of teaching' complement the principles of teaching and learning in the Western Australian Curriculum and Assessment Outline (https://k10outline.scsa.wa.edu.au/). The principles focus on the provision of a school and class environment that is intellectually, socially and physically supportive of learning. The principles assist whole-school planning and individual classroom practice.
Science provides an empirical way of answering interesting, relevant and important questions about the biological, physical and technological world. Students experience the joy of scientific discovery and explore their natural curiosity about the world around them. They develop critical and creative thinking skills and challenge themselves to identify questions and draw evidence-based conclusions using scientific methods.
The science curriculum develops an understanding of the nature of scientific inquiry and the ability to use a range of scientific inquiry methods. It allows students to develop the scientific knowledge, understandings and skills to make informed decisions about contemporary issues at the individual, local, national and global level.
Science teachers develop and plan engaging, relevant, inquiry-based lessons that integrate the three strands of Science Inquiry Skills, Science Understanding and Science as a Human Endeavour.
Figure 1 is a visual presentation of ‘ways of teaching’ Science.
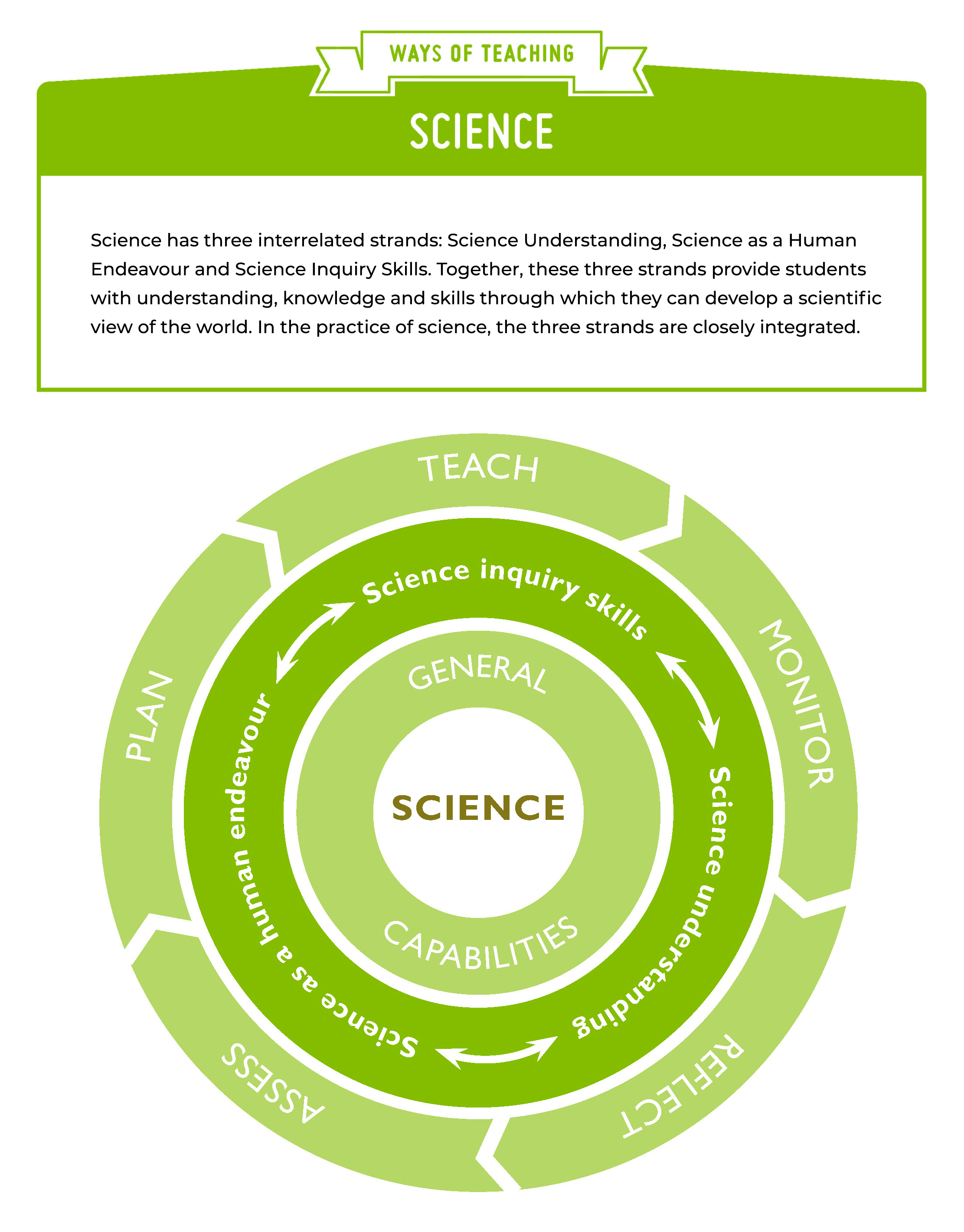
Science teachers provide a safe, positive and inclusive learning environment. The following table provides examples of learning experiences. The table is not exhaustive and teachers are encouraged to make professional decisions about the appropriate ways of teaching and learning experiences that best suit their classroom context.
Ways of teaching | Possible learning experiences |
Inquiry based, allowing students to observe and safely practise the processes and skills of science |
|
Connect prior knowledge and ideas to develop a deeper understanding of the world |
|
Use a diverse range of activities, both within a lesson and throughout the teaching program |
|
Provide an appropriate level of challenge that is fair, flexible and meaningful to students |
|
Use a range of technologies to enhance learning |
|

 Science Scope and Sequence (DOC) [v8.1]
Science Scope and Sequence (DOC) [v8.1]