Organisation
Content structure
The Western Australian Curriculum: Technologies learning area comprises two subjects:
- Design and Technologies
- Digital Technologies
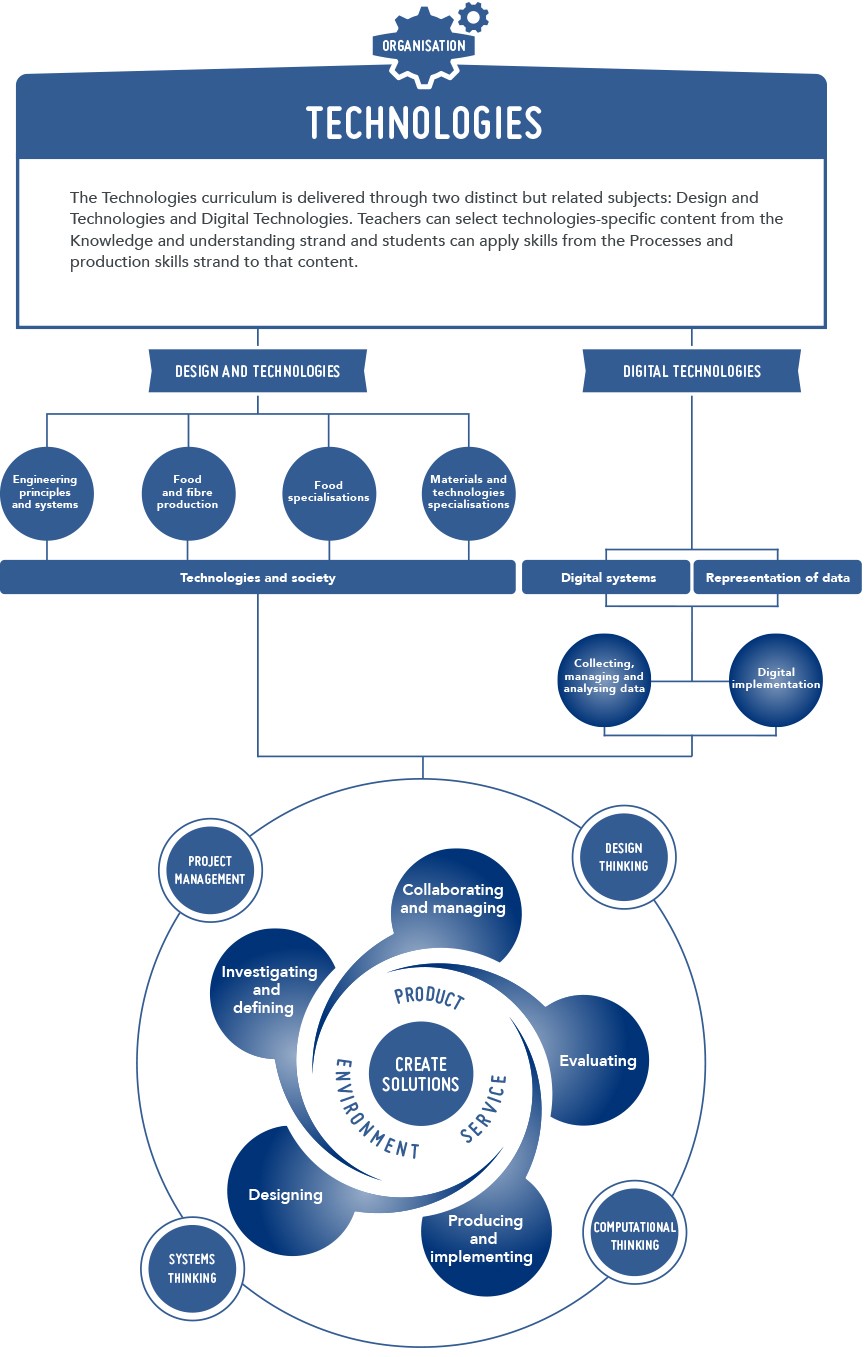
The Technologies curriculum is written on the basis that all students will study both Technologies subjects from Pre-primary to the end of Year 8. Within Design and Technologies (Engineering principles and systems; Food and fibre production; Food specialisations; Materials and technologies specialisations), students have the opportunity to study at least one of the contexts.
In Years 9 and 10 the study of Technologies is optional.
In Design and Technologies, it is desirable that schools provide students with the opportunity to engage with all contexts across Pre-primary to Year 10.
In Design and Technologies students learn about technologies in society through different technologies contexts (Engineering principles and systems; Food and fibre production; Food specialisations; and Materials and technologies specialisations) as they create designed solutions.
In Digital Technologies students are provided with practical opportunities to use design thinking and to be innovative developers of digital solutions and knowledge. Digital Technologies is a subject that has a specific curriculum and includes the practical application of the ICT general capability.
The syllabus for each of these subjects describes the distinct knowledge, understanding and skills of each subject and, where appropriate, highlights their similarities and complementary learning. This approach enables students to develop a comprehensive understanding of traditional, contemporary and emerging technologies. It also provides the flexibility, especially in the primary years of schooling, for developing integrated teaching programs that focus on both Technologies subjects and concepts and skills in other learning areas.
Relationship between the strands
Knowledge, understanding and skills in each subject are presented through two related strands:
- Knowledge and understanding
- Processes and production skills
Teachers select technologies-specific content from the Knowledge and understanding strand and students apply skills from the Processes and production skills strand to that content.
The common strand structure provides an opportunity to highlight similarities across the two subjects.
Knowledge and understanding
| Design and Technologies | Digital Technologies |
Technologies and society
Technologies and design across a range of technologies contexts:
| Digital systems
Representation of data
|
Table 1: Outlines the focus of the knowledge and understanding across the two Technologies subjects
Processes and production skills
| Design and Technologies | Digital Technologies |
Creating solutions by:
| Collecting, managing and analysing data
Digital implementation
Creating solutions by:
|
Table 2: Outlines the focus of the processes and production skills across the two Technologies subjects
|
| Figure 2: The organisation of content in the Technologies curriculum |
Year level descriptions
Year level descriptions provide an overview of the key concepts addressed, along with core content being studied at that year level. They also emphasise the interrelated nature of the two strands and the expectation that planning will involve integration of content from across the strands.
Content descriptions
Content descriptions set out the knowledge, understanding and skills that teachers are expected to teach and students are expected to learn. They do not prescribe approaches to teaching. The core content has been written to ensure that learning is appropriately ordered and that unnecessary repetition is avoided. However, a concept or skill introduced at one year level may be revisited, strengthened and extended at later year levels as needed.
Additional content descriptions are available for teachers to incorporate in their teaching programs. Schools will determine the inclusion of additional content, taking into account learning area time allocation and school priorities.
The additional content will not be reflected in the Achievement Standards.
Achievement standards
From Pre-primary to Year 10, achievement standards indicate the quality of learning that students should typically demonstrate by a particular point in their schooling. An achievement standard describes the quality of learning (e.g. the depth of conceptual understanding and the sophistication of skills) that would indicate the student is well-placed to commence the learning required at the next level of achievement.
Glossary
A glossary is provided to support a common understanding of key terms and concepts included in the core content.

 Technologies Scope and Sequence
Technologies Scope and Sequence