Ways of Teaching
The 'ways of teaching' aim to support teachers with planning for curriculum delivery across the years of school, with the teaching in each year extending learning in previous years.
The 'ways of teaching' complement the principles of teaching and learning in the Western Australian Curriculum and Assessment Outline (http://k10outline.scsa.wa.edu.au/). The principles focus on the provision of a school and class environment that is intellectually, socially and physically supportive of learning. The principles assist whole-school planning and individual classroom practice.
Making and Responding are intrinsically connected. Together they provide students with knowledge, understanding and skills as artists, performers and audience members and develop students' skills in critical and creative thinking. As students make in the Arts, they actively respond to their developing work and the works of others; as students respond in the Arts, they draw on the knowledge and skills acquired through their experience in making artworks.
Teachers have the freedom to apply aspects of the strands, Making and Responding, to plan teaching programs. Through the combination of both, teachers can provide rich opportunities to extend students' knowledge, skills and capacity to analyse and reflect. Responding occurs throughout the creative learning process.
To engage students in the Arts, teachers typically create learning experiences which:
- use all aspects of perception: sensory, emotional, cognitive, physical and relational to make learning experiential for students
- develop skills in students through modelling, coaching, practising and reflecting
- enable students to work individually and collaboratively, using flexible grouping to accommodate their needs and strengths
- encourage students to take risks and extend their ideas
- foster participation in projects in a flexible, dynamic learning environment
- provide opportunities for students to experience the Arts in live or virtual settings
- explore significant and recognisable examples of the Arts from different times and cultures to develop in students an aesthetic and cultural appreciation of the Arts.
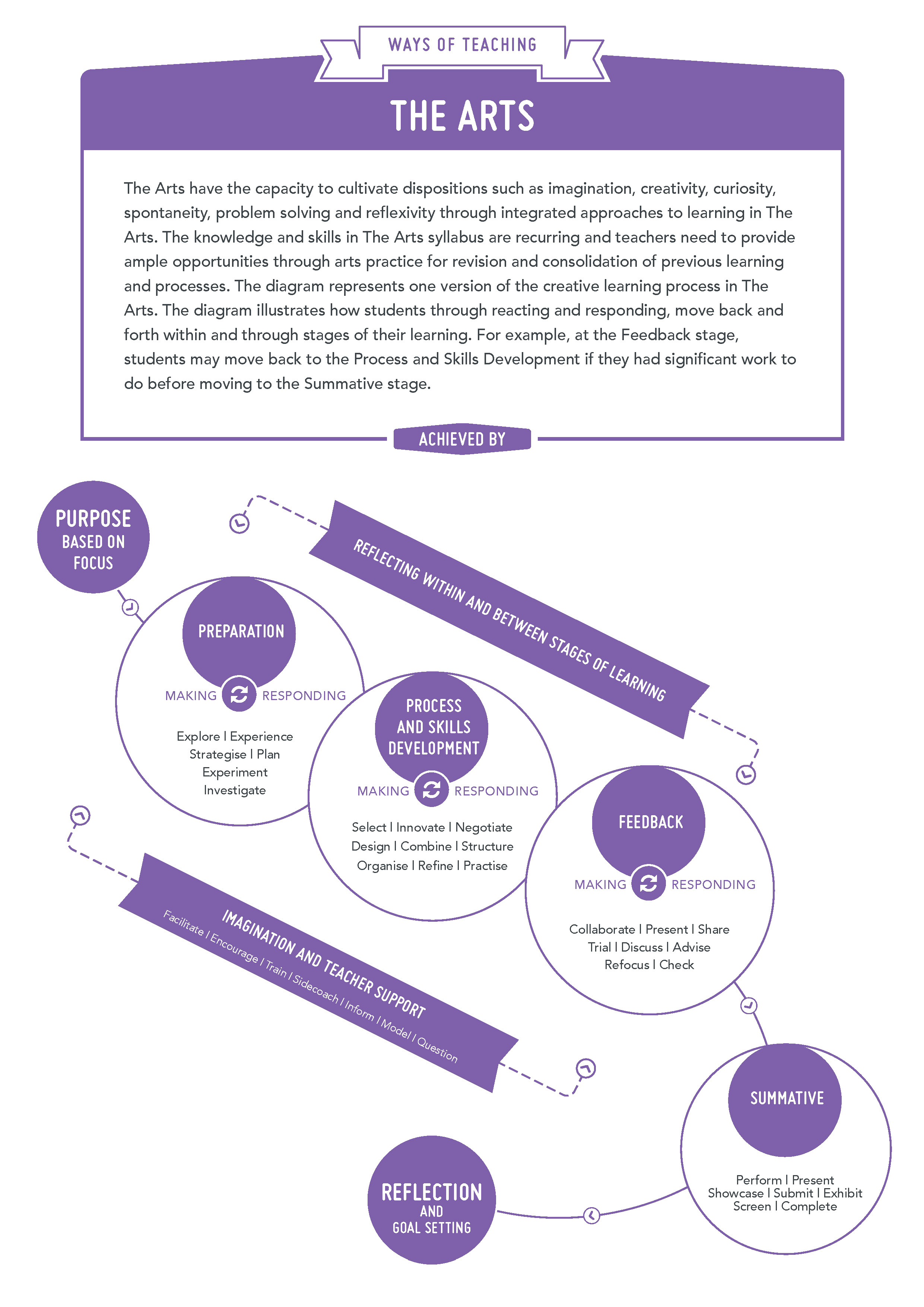
Many aspects of the Arts syllabus are recurring and teachers should provide ample opportunities through practice for revision and consolidation of previously introduced knowledge and skills. The diagram below presents one version of the creative learning process in the Arts.
Figure 1 is a visual representation of 'ways of teaching' in the Arts.
Safe working practices in the Arts are an essential aspect of the teaching and learning. These include providing or adapting an appropriate space to work; teaching students guiding principles to care for their voice and bodies; working safely with others and with specialist equipment; and appropriate warm-up procedures before class or a performance. Safe working practices also include the responsibility teachers and students have in the maintenance of safe social and emotional spaces for the Arts. Without this aspect of safe working practices, risk-taking becomes difficult for many students. To ensure the development of creative processes where students are willing to risk making mistakes in the Arts, teachers will need to establish and maintain a safe learning environment in the classroom.
Although Dance, Drama, Media Arts, Music, and Visual Arts are distinct subjects in the Arts, teachers may create opportunities for students to study and make artworks that feature a fusion of traditional art forms and practices to develop hybrid and/or cross-arts projects. This learning involves the exploration of traditional and contemporary arts practices, including those from different cultures that acknowledge community and cultural protocols. Such works might:
- combine performance, audio and/or visual aspects
- combine processes typical of the different Arts subjects
- involve other learning areas
- exist in physical, digital or virtual spaces
- combine traditional, contemporary and emerging media and materials
- be created individually or collaboratively.
Teachers in schools are the key to providing students with rich, sustained, rigorous learning in each of the subjects in The Arts. The Arts industry complements the provision of the Arts syllabus in schools through programs and partnerships. The industry increasingly provides specialist services for schools, as appropriate, through experiences such as visiting performances; demonstrations and exhibitions; artists in residence; professional development for teachers; and access for students and teachers to specialised facilities in galleries, concert halls, theatres and other arts venues.
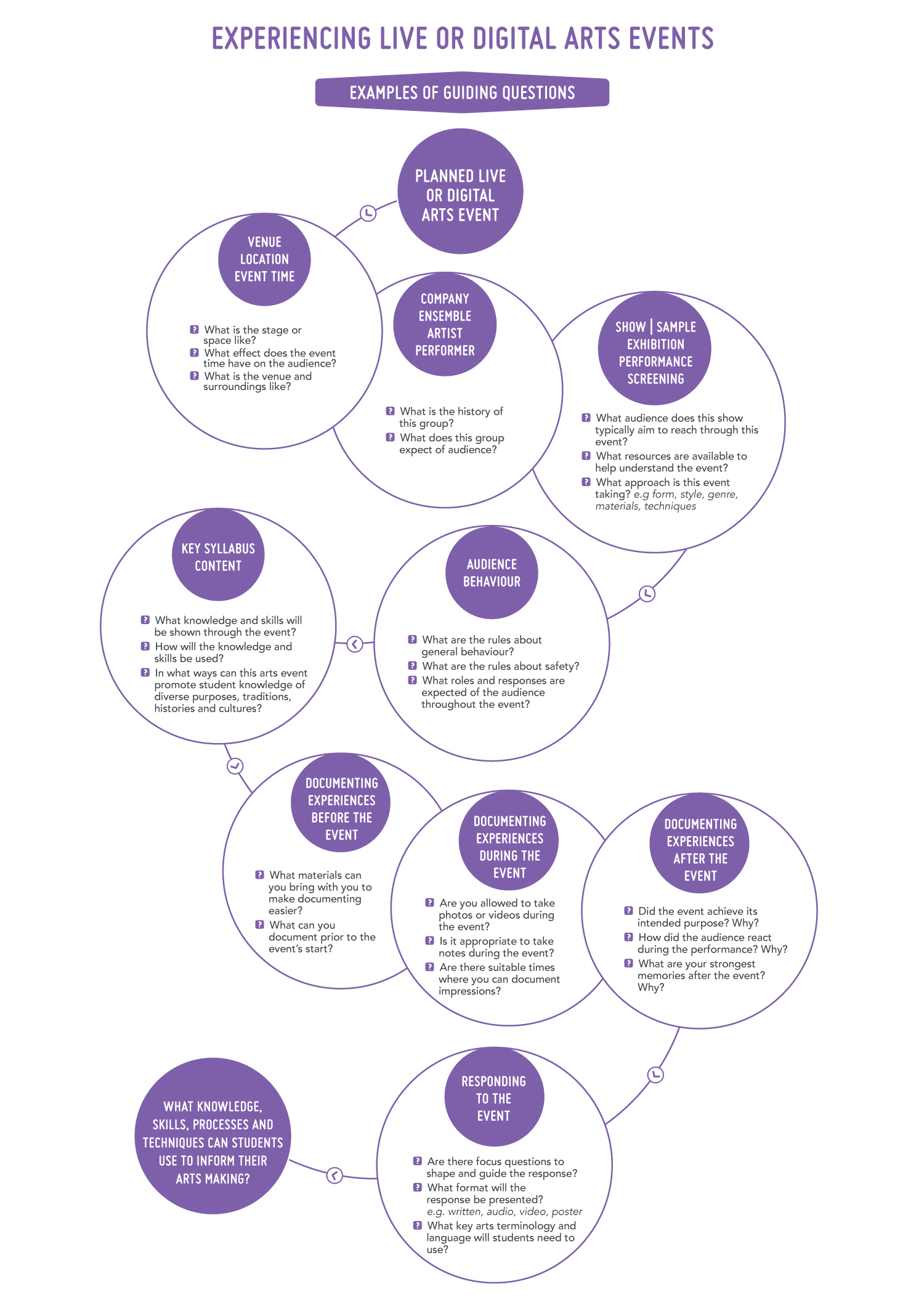
Figure 2 is a visual representation of guiding questions whilst experiencing live or digital arts events.
For information on how to collect evidence to inform planning for ongoing learning experiences in the Arts, refer to 'Ways of Assessing'.

 The Arts Scope and Sequence
The Arts Scope and Sequence